Introvert and Extrovert: A glamorous social event OR a quiet evening at home with your favorite book? If you chose the former – then you’re an extrovert, and if the latter – then you’re an introvert. Unlike extroverts, introverts prefer pets over people and deep conversations over small talks. But, do you know that these behavioral preferences are the result of differences in the structure of your brain?
Yes, an introvert brain is wired differently.
Introverts Vs Extroverts
Introverts and extroverts are the terms used to define two very contrasting personality types. The terms were coined by the famous psychiatrist, Carl Jung, in the 1920s. Extroverts and introverts differ in the way they are energized.
While extroverts gain energy from social interactions and stimulating external environments, introverts are overwhelmed by these things. They prefer quiet and solitary environments and need alone time to unwind. Usually, people are not completely extroverted or introverted, but a mixture of both. However, everyone is more inclined towards a particular personality type.

Related: 19 Signs You’re an Introvert in a Loud World
Now, let’s dig deeper into the biochemical story and brain structure of these two personality types. Read on to know why introverts and extroverts think and behave differently.
1. Difference In The Blood Flow To The Brain
There are different types of neurotransmitters in the brain. Each neurotransmitter has a certain pathway in the brain, through which it travels and directs where the blood circulates and regulates how much of it flows to different brain regions. Further, the route and quantity of the blood flow influence what parts of the brain and central nervous centers are “turned on”. The part of the brain systems activated determines our response to the world and behavior.
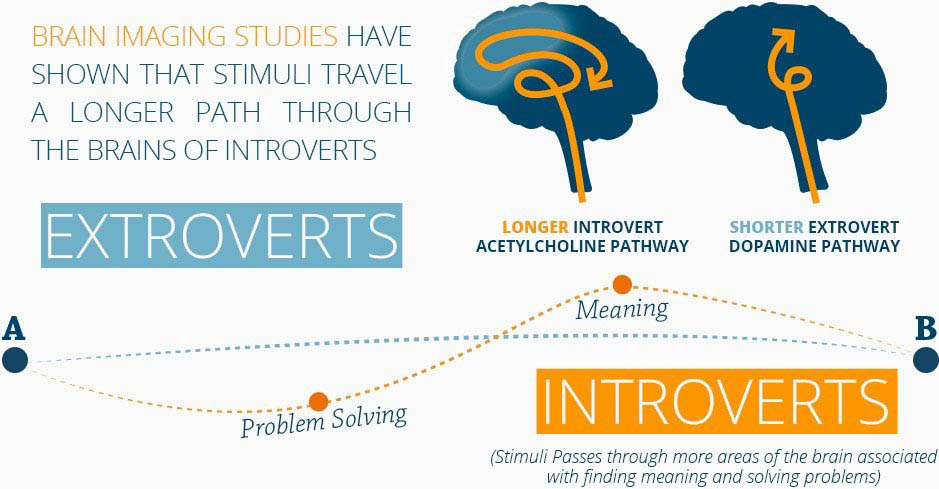
In an experiment, introverts and extroverts were asked to lie down and relax while a very small dose of radioactivity was injected into their bloodstream. When their brains were scanned, it was found that introverts have more blood flow to their brains. Also, the blood traveled along different pathways in the introvert’s and extrovert’s brains.
While the extrovert attended externally to what was happening in the lab, the introverts were attending to their internal thoughts and feelings. It seems the introvert’s pathway is more complicated than that of extroverts.
2. Extroverts Rely On Neurotransmitter Dopamine
Dopamine, a crucial neurotransmitter, is a sort of reward for the brain and also influences our mood and feelings. It motivates people to achieve things and seek rewards. When dopamine is secreted, we become more alert to the activities in our surroundings and motivated to undertake behaviors that are considered risky.
Dopamine produces an instant feeling of euphoria in us when an externally rewarding situation happens.
This chemical in our brains plays an important role in the behavioral differences between introverts and extroverts. The amounts of dopamine secreted are the same for introverts as well as extroverts. But the way both of these personalities react to the dopamine secreted is different.
There is a clear difference in the dopamine reward network, which is more active in an extrovert brain. Extroverts are known to have a shorter dopamine pathway. Information from the outside world like sound, images, light travels a shorter pathway ( i.e – “quick response” areas of the brain where taste, touch, sight, and sound are processed), before entering an extrovert’s brain.
Therefore, asking a girl for a date, talking to strangers, taking risks comes quite easily to extroverts than introverts. It’s the dopamine, that extroverts are always enthusiastic about new endeavors and feel rewarded socializing with people. Dopamine and intensity of the stimulation act as a cue that they are achieving their goals.
Extroverts have low sensitivity to dopamine, so they need this chemical in large amounts. On the other hand, introverts are highly sensitive to dopamine and feel overstimulated, according to the 2002 book, The Introvert Advantage, by Dr. Marti Olsen Laney.
Related: How to Supercharge Your Dopamine Levels Naturally
3. Introverts Rely On Neurotransmitter Acetylcholine
Introverts are more dependent on acetylcholine, which is also a neurotransmitter, but it is slightly different than how dopamine works. Acetylcholine, like dopamine, is a reward-inducing neurotransmitter, but the reward is more internal.
When acetylcholine is secreted it encourages a person to introspect and helps one feel relaxed and content. It also enables a person to concentrate on one particular task like reading books or walking. It is easier to turn inwards when there is no external stimulation.
That is why introverts prefer a quieter environment so that they can experience the reward of acetylcholine, which works better in calmer environments.
Some other studies have found that cortical neurons of introverts and extroverts may respond differently to the neurotransmitter chemicals gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and N-methyl D-aspartate (NMDA). This is an interesting connection because both GABA and NMDA have been linked to anxiety disorders.
Related: 15 Extroverted Behaviors That Annoy An Introvert The Most
4. Difference In Gray Matter
The prefrontal cortex is a part of the brain that monitors a number of activities, like social behavior, abstract thought, and decision making. It is also the seat of personality traits. This region contains gray matter – a brain tissue where most of the brain activity takes place.
Introverts contain a higher amount of grey matter in their prefrontal cortexes as compared to extroverts. Also, introverts have gray matter that’s denser on average than extroverts.
How does this affect behavior?
Introverts find it more rewarding to focus deeply on abstract topics whereas extroverts are all about enjoying the present moment.
In a study by Cornell University scientists, the team of investigators gathered a mixed sample of introverts and extroverts and randomly split these volunteers into two groups. The first group took the stimulant Ritalin, while the second group took a placebo. All the participants then watched a series of videos such as random landscape shots and forest scenes. The same test was again performed after three days without drugs. Researchers measured the subjects’ alertness and demeanor.
Extroverts who’d taken Ritalin were excited watching videos even in the absence of the drug. But introverts weren’t happier or more alert post-video, regardless of whether they’d taken Ritalin or not. The finding is rooted in a crucial difference between the ways introverts and extroverts process feelings of excitement.
Extroverts, associate feelings of reward with their immediate environment, whereas introverts tend to associate them with their inner thoughts or may interpret them as anxiety rather than excitement.


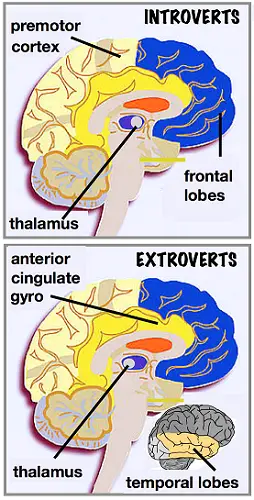
5. Differences In Frontal Lobes And Amygdala
One a 2006 study, PET scans of introverts showed more activity in the brain frontal lobes. This brain region is activated for remembering, problem-solving, and planning. Extroverts show greater activity in the brain’s anterior lobes. This brain region involves external stimulated sensory processing like hearing, watching, or driving.
Some studies showed that the right-hemisphere amygdala tends to be larger in extroverts than in introverts, as does the anterior cingulate cortex—except in female extroverts, whose anterior cingulate cortices are apparently smaller than those of female introverts.
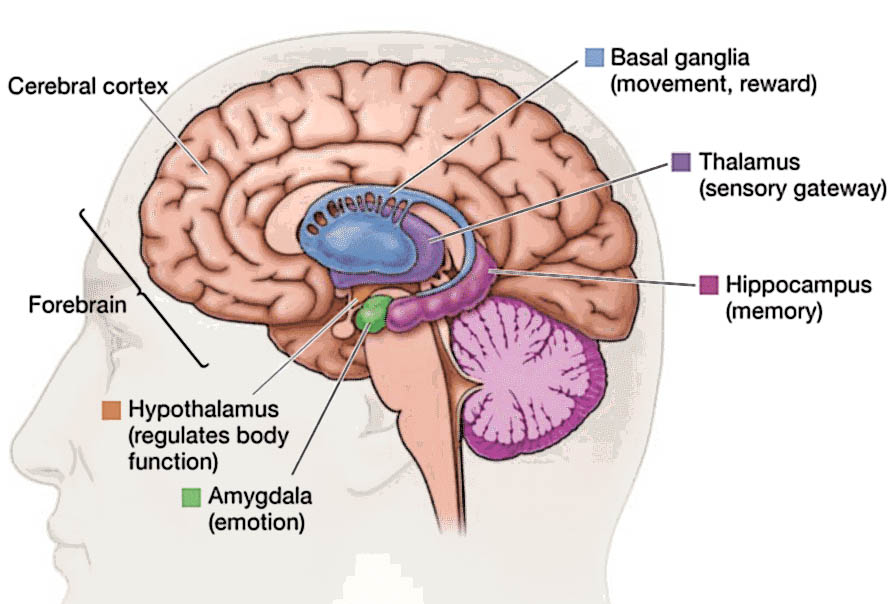
Although many studies have highlighted the anterior cingulate in social error detection, it is not clearly understood how introverts and extroverts process social missteps. Researchers have found that an introvert’s premotor cortex tends to process stimuli more quickly when compared to an extrovert.
Related: 15 Common Cognitive Distortions That Twist Your Thinking
6. Introverts Prefer One Type Of The Nervous System More Than The Other
There are two parts of the nervous system- sympathetic and parasympathetic.
The sympathetic side is responsible for the “fight, fright and flight” mode. It prepares the body for action, triggers the release of adrenaline, pumps glucose to the muscles to energize them, and the oxygen levels of the body are increased. The thinking process is temporarily halted and the neurotransmitter dopamine boosts alertness in the backside of the brain.
The parasympathetic nervous system, on the other hand, relaxes muscles, conserves energy, and boosts food metabolism. It triggers the release of acetylcholine, which in turn increases blood flow to the front of the brain and keeps it alert.
Besides dopamine, extroverts also need their sidekick adrenaline, to make more dopamine in the brain. So, extroverts are linked with the dopamine/adrenaline, energy-spending, sympathetic nervous system. However, introverts prefer to use the acetylcholine, energy-conserving, parasympathetic nervous system. This is what enables introverts to act calmly and take decisions in a measured way.
Summing Up
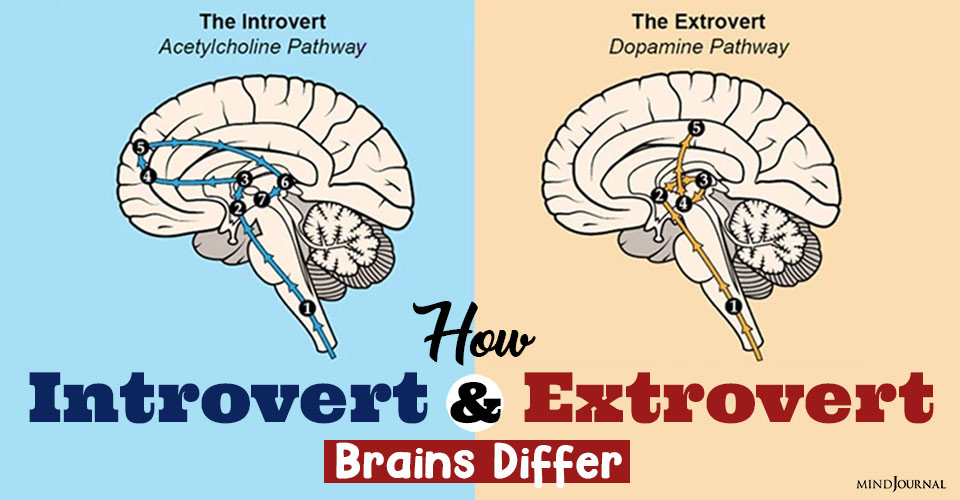
The information received by an introvert’s brain from the external world travels through a longer pathway called the acetylcholine pathway. In this pathway, the information crosses many different areas, like the right front insular, which is involved with empathy, emotions, and introspection, then the Broca’s region, which is responsible for self-talk, words, and speech. It also crosses the right and left frontal lobes and the hippocampus, each having individual functions.
On the other hand, information in the extrovert brain passes through the shorter pathway called the dopamine pathway, which crosses regions in the brain that process sight, sound, taste, and touch. The acetylcholine pathway, which the information in an introvert’s brain takes, is much longer than the dopamine pathway. Hence, introverts take more time to respond and speak and tend to overthink things.
Now that you know that the makeup of your brain is different, it will probably make more sense to you that you naturally prefer quieter and more peaceful environments and avoid highly stimulating environments.
References:
Laney, M.O., 2002. The introvert advantage: How to thrive in an extrovert world. Workman Publishing. Vorkapić, S.T., 2017. The Proposal of Investigating the Possible Extraversion Effect in the Neurofeedback. Baik, S.H., Yoon, H.S., Kim, S.E. and Kim, S.H., 2012. Extraversion and striatal dopaminergic receptor availability in young adults: an [: 18: F] fallypride PET study. Neuroreport, 23(4), pp.251-254. Martin, E., 2014. Tips for Teaching: The Brain Game: Teaching Strategies for Introverted vs. Extroverted Students. Bulletin for the Study of Religion, 43(3), pp.39-46. Khalil, R., 2016. Influence of extroversion and introversion on decision-making ability. International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences, 4(5), pp.1534-1538. Berridge, K.C., 2004, April. Pleasure, unfelt affect, and irrational desire. In Feelings and emotions: The Amsterdam symposium (pp. 423-454). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Cohen, M.X., Young, J., Baek, J.M., Kessler, C. and Ranganath, C., 2005. Individual differences in extraversion and dopamine genetics predict neural reward responses. Cognitive brain research, 25(3), pp.851-861. Fu, Y., 2013. On the nature of extraversion: variation in conditioned contextual activation of dopamine-facilitated affective, cognitive, and motor processes. Frontiers in human neuroscience, 7, p.288. Holmes, A.J., Lee, P.H., Hollinshead, M.O., Bakst, L., Roffman, J.L., Smoller, J.W. and Buckner, R.L., 2012. Individual differences in amygdala-medial prefrontal anatomy link negative affect, impaired social functioning, and polygenic depression risk. Journal of Neuroscience, 32(50), pp.18087-18100.










Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.