Mental disorders and their reflections on the art of typography
Slovak graphic designer Igor Kupec suffered from generalized anxiety disorder and panic attacks during his college years.
In his words, “When I was a university student I suffered from generalized anxiety disorder and panic attacks. It was a hard period of my life, but after all – also very enriching. After a few years, I started to think about mental disorders from the perspective of a graphic designer. My “personal quest” was to catch the essence of disorders by typography. I was able to visualize many of them, except the one I was struggling with.”
He then started to design typographic images for mental disorders. The article has compiled them for you. Check them out and let us know if you could relate to it.
Here are 20 mental disorders and their reflections on the art of typography
1. Bipolar Disorder

Bipolar disorder, formerly manic depression, is a mental disorder with periods of depression and periods of elevated mood. The elevated mood is significant and is known as mania or hypomania, depending on its severity, or whether symptoms of psychosis are present. During mania, an individual behaves or feels abnormally energetic, happy, or irritable. Individuals often make poorly thought out decisions with little regard to the consequences. The need for sleep is usually reduced during manic phases. During periods of depression, there may be crying, a negative outlook on life, and poor eye contact with others.
Related: Are Medications The Only Solution To Mental Illness?
2. Occupational Burnout

Burnout is a type of psychological stress. Occupational burnout or job burnout is characterized by exhaustion, lack of enthusiasm and motivation, feelings of ineffectiveness, and also may have the dimension of frustration or cynicism, and as a result reduced efficacy within the workplace.
3. Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
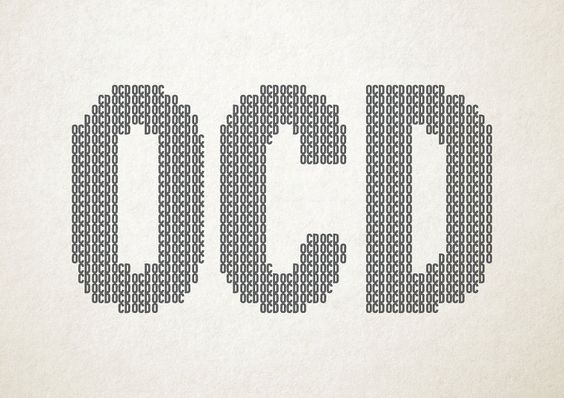
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is a mental disorder where people feel the need to check things repeatedly, perform certain routines repeatedly, or have certain thoughts repeatedly. People are unable to control either the thoughts or the activities for more than a short period of time. Common activities include hand washing, counting of things, and checking to see if a door is locked. These activities occur to such a degree that the person’s daily life is negatively affected. Most adults realize that behaviors do not make sense.
4. Tourette Syndrome
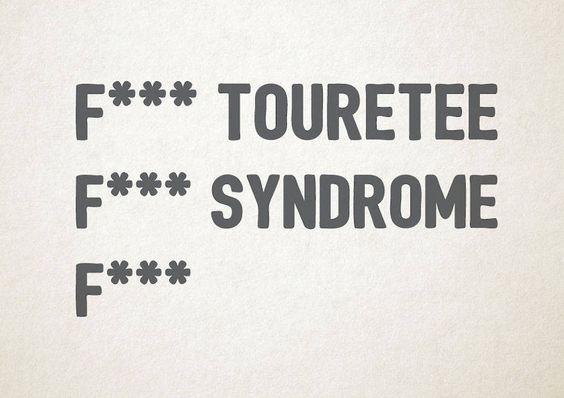
Tourette syndrome is an inherited neuropsychiatric disorder characterized by multiple physical tics and at least one vocal tic. These tics characteristically wax and wane, can be suppressed temporarily, and are preceded by a premonitory urge. Tourette’s was once considered a rare and bizarre syndrome, most often associated with the exclamation of obscene words or socially inappropriate and derogatory remarks (coprolalia), but this symptom is present in only a small minority of people with Tourette’s. Tourette’s is no longer considered a rare condition, but it is not always correctly identified because most cases are mild and the severity of tics decreases for most children as they pass through adolescence.
5. Schizophrenia

Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by abnormal social behavior and failure to understand what is real. Common symptoms include false beliefs, unclear or confused thinking, hearing voices, reduced social engagement, and emotional expression, and a lack of motivation. People with schizophrenia often have additional mental health problems such as anxiety disorders, major depressive illness, or substance use disorder. Symptoms typically come on gradually, begin in young adulthood, and last a long time.
Related: Schizophrenia Test: If You Can See Through These Optical Illusions You Might Have Schizotypy Traits
6. Stage Fright

Stage fright or performance anxiety is the anxiety, fear, or persistent phobia which may be aroused in an individual by the requirement to perform in front of an audience, whether actually or potentially (for example, when performing before a camera). In the context of public speaking, this may precede or accompany participation in any activity involving public self-presentation.
In some cases, stage fright may be a part of a larger pattern of social phobia (social anxiety disorder), but many people experience stage fright without any wider problems. Quite often, stage fright arises in mere anticipation of a performance, often a long time ahead. It has numerous manifestations: fluttering or pounding heart, tremor in the hands and legs, sweaty hands, facial nerve tics, dry mouth, and dizziness.
7. Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)

Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder is characterized by problems paying attention, excessive activity, or difficulty controlling behavior which is not appropriate for a person’s age. These symptoms begin by age six to twelve, are present for more than six months and cause problems in at least two settings (such as school, home, or recreational activities).
8. Graphomania

Graphomania refers to an obsessive impulse to write. When used in a specifically psychiatric context, it labels a morbid mental disorder that results in writing rambling and confusing statements, often degenerating into a meaningless succession of words or even nonsense and called then graphorrhea.
9. Depression

Depression is a state of low mood and aversion to activity that can affect a person’s thoughts, behavior, feelings, and sense of well-being. People with a depressed mood can feel sad, anxious, empty, hopeless, helpless, worthless, guilty, irritable, angry, ashamed, or restless. They may lose interest in activities that were once pleasurable, experience loss of appetite or overeating, have problems concentrating, remembering details or making decisions, experience relationship difficulties and may contemplate, attempt or commit suicide. Insomnia, excessive sleeping, fatigue, aches, pains, digestive problems, or reduced energy may also be present.
Related: Escaping the Matrix of Depression: The Hidden Antidote That Will Set You Free
10. Dysgraphia

Dysgraphia is a deficiency in the ability to write, primarily handwriting, but also coherence. Dysgraphia is a transcription disability, meaning that it is a writing disorder associated with impaired handwriting, orthographic coding (orthography, the storing process of written words and processing the letters in those words), and finger sequencing (the movement of muscles required to write). It often overlaps with other learning disabilities such as speech impairment, attention deficit disorder, or developmental coordination disorder.
11. Insomnia

Insomnia is a sleep disorder where people have trouble sleeping. They may have difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep as long as desired. Insomnia is typically followed by daytime sleepiness, low energy, irritability, and a depressed mood. It may result in an increased risk of motor vehicle collisions, as well as problems focusing and learning. Insomnia can be short term, lasting for days or weeks, or long term, lasting more than a month.
Related: Insomnia 101: Causes, Symptoms Of Insomnia & How To Sleep Better
12. Bulimia

Bulimia nervosa, also known as simply bulimia, is an eating disorder characterized by binge eating followed by purging. Binge eating refers to eating a large amount of food in a short amount of time. Purging refers to the attempts to get rid of the food consumed. This may be done by vomiting or taking laxatives. Other efforts to lose weight may include the use of diuretics, stimulants, water fasting, or excessive exercise. Most people with bulimia are at a normal weight. The forcing of vomiting may result in thickened skin on the knuckles and breakdown of the teeth.
13. Anorexia

Anorexia nervosa often referred to simply as anorexia, is an eating disorder characterized by a low weight, fear of gaining weight, a strong desire to be thin, and food restriction. Many people with anorexia see themselves as overweight even though they are in fact underweight. If asked they usually deny they have a problem with low weight. Often they weigh themselves frequently, eat only small amounts, and only eat certain foods. Some will exercise excessively, force themselves to vomit, or use laxatives to produce weight loss.
14. Phobia

A phobia is a type of anxiety disorder, defined by a persistent fear of an object or situation. The phobia typically results in a rapid onset of fear and is present for more than six months. The affected person will go to great lengths to avoid the situation or object, typically to a degree greater than the actual danger posed. If the feared object or situation cannot be avoided, the affected person will have significant distress.
Related: 100+ Types Of Common, Unique and Bizarre Phobias
15. Parkinson’s Disease

Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a long term mental disorder of the central nervous system that mainly affects the motor system. Early in the disease, the most obvious are shaking, rigidity, slowness of movement, and difficulty with walking. Thinking and behavioral problems may also occur. Dementia becomes common in the advanced stages of the disease. Depression and anxiety are also commonly occurring in more than a third of people with PD. Other symptoms include sensory, sleep, and emotional problems.
16. Addiction

Addiction is a medical condition characterized by compulsive engagement in rewarding stimuli, despite adverse consequences. The two properties that characterize all addictive stimuli are that they are reinforcing (i.e., they increase the likelihood that a person will seek repeated exposure to them) and intrinsically rewarding (i.e., perceived as being positive or desirable).
17. Narcissistic Personality Disorder

Narcissistic personality disorder (NPD) is a long-term pattern of abnormal behavior characterized by exaggerated feelings of self-importance, an excessive need for admiration, and a lack of understanding of others’ feelings. People affected by it often spend a lot of time thinking about achieving power or success, or about their appearance. They often take advantage of the people around them.
18. Megalomania

Megalomania is often used loosely to mean having delusional fantasies of wealth, power, or omnipotence.
19. Paranoia

Paranoia is a thought process believed to be heavily influenced by anxiety or fear, often to the point of delusion and irrationality. Paranoid thinking typically includes persecutory, or beliefs of conspiracy concerning a perceived threat towards oneself (e.g. “Everyone is out to get me”).
Related: Ways in Which Childhood Bullying Has Lifelong Effects on a Child’s Mental Health
Paranoia is distinct from phobias, which also involve irrational fear, but usually no blame. Making false accusations and the general distrust of others also frequently accompany paranoia. For example, an incident most people would view as an accident or coincidence, a paranoid person might believe was intentional.
20. Alzheimer’s Disease

Alzheimer’s disease (AD), is a chronic neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and gets worse over time. It is the cause of 60% to 70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events (short-term memory loss). As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems with language, disorientation (including easily getting lost), mood swings, loss of motivation, not managing self-care, and behavioral issues.
Did you like these typography images for mental disorders? Let us know in the comments.
Some rare mental illnesses are-
- Apotemnophilia – overwhelming desire to amputate healthy parts of [the] body.
- Stendhal Syndrome – People experience physical and emotional anxiety as well as confusion, dissociative experiences, and hallucinations when exposed to art.
- Diogenes Syndrome – It mainly affects older adults and is characterised by excessive hoarding, dirty homes, and poor personal hygiene.
- Clinical Lycanthropy – Affected person believes that s/he can transform into an animal.
- Khyâl cap or “wind attacks” – is chracterised by shortness of breath, dizziness, palpitations, and cold extremities
References:
- Goldberg, D.P. and Huxley, P., 1992. Common mental disorders: a bio-social model. Tavistock/Routledge.
- Edition, F., 2013. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. Am Psychiatric Assoc.
- Gatz, M., Kasl-Godley, J.E. and Karel, M.J., 1996. Aging and mental disorders.










Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.