Are the effects of trauma worse than the trauma itself? The following article will help to identify the signs of unresolved childhood trauma in adults and heal your relationships.
In this blog, we will cover:
- Unresolved trauma meaning
- Unresolved trauma examples
- Unresolved childhood trauma
- Signs of unresolved childhood trauma in adults
- Unresolved trauma and relationships
Trauma is a deeply distressing experience that can have long-lasting effects on an individual’s mental, emotional, and physical well-being, especially if it’s unresolved childhood trauma.
Unresolved childhood trauma in adults manifests in various ways. While some people are able to process and heal from their traumatic experiences, others may find themselves struggling to move forward, resulting in unresolved trauma.
Unresolved Trauma Meaning
Unresolved trauma refers to the lingering effects of traumatic events that continue to impact a person’s life, often manifesting in various warning signs.
By recognizing these signs, individuals and their loved ones can take proactive steps toward seeking help and finding healing.

Unresolved Trauma Examples
- Childhood abuse (physical, sexual, or emotional)
- Domestic violence
- Sexual assault or rape
- Military combat experiences
- Natural disasters (e.g., hurricanes, earthquakes)
- Serious accidents or injuries
- Witnessing or experiencing a violent crime
- Neglect or abandonment in childhood
- Medical trauma (e.g., surgeries, life-threatening illnesses)
- Loss of a loved one through death or separation
- Bullying or harassment
- Racial or ethnic discrimination
- Persistent exposure to community violence
- Combatting or surviving terrorism or war
- Cult involvement or religious trauma
- Childhood neglect or emotional deprivation
7 Warning Signs Of Unresolved Childhood Trauma In Adults
These are the seven signs you have unresolved childhood trauma:

1. Flashbacks and Intrusive Memories:
One of the most common signs of unresolved childhood trauma in adults is the re-experiencing of traumatic events through flashbacks or intrusive memories.
These can be triggered by certain sights, sounds, smells, or even thoughts associated with the traumatic event. Flashbacks can be incredibly vivid, making the individual feel as though they are reliving the trauma, leading to heightened anxiety and distress.
2. Avoidance Behaviors:
Unresolved childhood trauma in adults often develops avoidance behaviors as a coping mechanism. Individuals may go to great lengths to avoid situations, people, or places that remind them of the traumatic event.
This can lead to social withdrawal, isolation, and difficulty in participating in activities they once enjoyed. Avoidance behaviors can prevent individuals from fully engaging in their lives and hinder their ability to form meaningful connections with others.
3. Emotional Dysregulation:
Carrying unresolved anger from childhood is also a common sign. Unresolved childhood trauma in adults can significantly impact emotional well-being, resulting in intense and unpredictable emotions.
People may experience frequent mood swings, have difficulty managing anger or irritability, or struggle with persistent feelings of sadness or emptiness.
Emotional dysregulation can also manifest as a heightened startle response, excessive fear or anxiety, and a general sense of being on edge.
4. Hypervigilance and Hyperarousal:
Unresolved childhood trauma in adults often manifests as hypervigilance and hyperarousal, which means being constantly on high alert for potential threats.
They may have difficulty relaxing, experience sleep disturbances, and find it challenging to concentrate or focus on daily tasks. This state of heightened vigilance can be exhausting and make it challenging to feel safe and secure in their environment.
5. Negative Self-Perception:
Unresolved childhood trauma in adults can significantly affect self-perception and self-worth. People may develop negative beliefs about themselves, feeling guilt, shame, or self-blame for the traumatic event.
This negative self-perception can lead to a loss of confidence, self-isolation, and difficulties in forming and maintaining healthy relationships.
6. Physical Symptoms:
Trauma doesn’t just affect the mind and emotions but can also have physical manifestations.
Physical symptoms of unresolved trauma can include headaches, stomachaches, chronic pain, fatigue, and changes in appetite or sleep patterns.
These physical symptoms can be a direct result of the unresolved trauma or can be psychosomatic, stemming from the mind-body connection.
7. Substance Abuse and Self-Destructive Behaviors:
In an attempt to cope with the overwhelming pain and distress of their unresolved childhood trauma, individuals may turn to substance abuse or engage in self-destructive behaviors.
Alcohol or drug dependency, reckless driving, self-harm, or disordered eating patterns can serve as unhealthy coping mechanisms to numb emotional pain temporarily.
These behaviors, however, only perpetuate the cycle of trauma and can lead to further complications.
Some more unresolved trauma symptoms in adults
Here are some more signs of unresolved childhood trauma:

- Emotional flashbacks or intense emotional reactions to certain triggers
- Difficulty forming and maintaining healthy relationships
- Low self-esteem and self-worth
- Trust issues and fear of intimacy
- Avoidance of certain situations or places that remind them of the trauma
- Persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, or emptiness
- Chronic anxiety, hypervigilance, or a constant sense of danger
- Mood swings and difficulty regulating emotions
- Self-destructive behaviors, such as self-harm or substance abuse
- Sleep disturbances, including nightmares or insomnia
- Physical symptoms such as headaches, stomachaches, or unexplained chronic pain
- Difficulty setting and maintaining boundaries in relationships
- Dissociation or feeling disconnected from oneself or reality
- Negative self-perception and self-blame
- Difficulty with trust and establishing a sense of safety
- Problems with intimacy and sexual functioning
- Difficulty in managing anger and impulsivity
- Problems with concentration, memory, and decision-making
- Persistent feelings of guilt or shame
- Engaging in repetitive or compulsive behaviors as a way to cope
Unresolved childhood trauma in adults can keep them from living their best life and living up to their full potential. So if you or someone you love is showing the symptoms of unresolved childhood trauma, do not overlook them, and seek help!
Read 10 Ways To Overcome Childhood Trauma: Grow Beyond Your Childhood Trauma And Reclaim Your Life
Unresolved Trauma And Relationships
Unresolved childhood trauma can have a profound impact on adult relationships, often leading to significant challenges and difficulties.
Unresolved childhood trauma in adults can result in a struggle with trust and intimacy, people find it challenging to form and maintain healthy connections with others.
The fear of being hurt or betrayed again can make it difficult for them to open up emotionally or establish a sense of vulnerability in relationships.
Unresolved childhood trauma can also manifest in patterns of avoidance, where individuals may withdraw from close relationships, fearing that they will be reminded of or retraumatized by certain triggers.
This can result in feelings of isolation, loneliness, and a sense of disconnection from others.
Additionally, unresolved trauma can contribute to emotional dysregulation, causing individuals to have difficulty managing their emotions, leading to conflicts and strained communication within relationships.
It is crucial for individuals with unresolved childhood trauma to seek professional support and engage in therapy to address these challenges, heal from their past experiences, and develop healthier relationship patterns.
So, how to heal unresolved childhood trauma?
Read Do You Have Abandonment Issues? 20 Telltale Signs And Coping Tips
Healing Unresolved Trauma
Recognizing the warning signs of unresolved trauma is the first step toward seeking help and finding healing.
If you or someone you know exhibits these signs, it is crucial to reach out to a mental health professional specializing in trauma.
Trauma-focused therapies, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR), or other evidence-based therapies like somatic experiencing or trauma-focused expressive arts therapy, can be highly effective in addressing unresolved trauma.
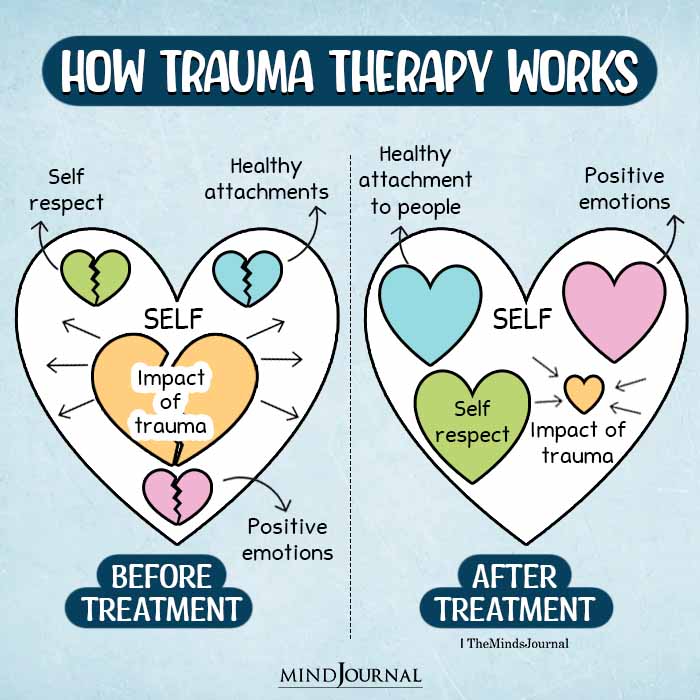
In addition to seeking professional help, there are some steps individuals can take to support their healing journey:
- Practice Self-Care: Engage in activities that promote self-care and self-compassion. This may include regular exercise, maintaining a balanced diet, getting enough sleep, and engaging in activities that bring joy and relaxation. Taking care of your physical and emotional well-being can help build resilience and provide a solid foundation for healing.
- Establish a Support System: Reach out to trusted friends, family members, or support groups who can provide a safe space for you to express your feelings and share your experiences. Having a supportive network can help alleviate feelings of isolation and provide validation and understanding.
- Educate Yourself: Learn about trauma and its effects to gain a better understanding of your experiences. Knowledge empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their healing journey and can help reduce self-blame or guilt associated with unresolved trauma. Get a free online trauma assessment too.
- Practice Mindfulness and Grounding Techniques: Incorporate mindfulness and grounding techniques into your daily routine. These practices can help you stay present at the moment, manage anxiety, and regulate overwhelming emotions. Deep breathing exercises, meditation, and sensory grounding techniques (such as focusing on your senses or engaging in calming activities) can be helpful tools.
- Explore Creative Outlets: Engaging in creative outlets like writing, painting, music, or dance can provide a means of expression and catharsis. Creative activities allow for the release of emotions and can help process unresolved trauma in a non-verbal and symbolic way.
- Prioritize Safety and Boundaries: Establish and enforce healthy boundaries in your relationships and environments. Creating a sense of safety is essential for healing from trauma. Recognize when certain situations or relationships are triggering and take steps to protect yourself from further harm.
Remember, identifying the signs of unresolved trauma and healing from trauma is a personal and unique journey. There is no timeline for healing, and progress may occur at different rates for different individuals.
Be patient and kind to yourself throughout the process, and remember that seeking professional support is an important step toward reclaiming your life and finding peace.
If you or someone you know is struggling with unresolved trauma and its effects, it’s important to reach out to a mental health professional or helpline in your country for assistance. You don’t have to face it alone, and support is available to help you on your path to healing and recovery.
Read The 4 Types Of Trauma Responses And How To Reclaim Your Life
So, those were the signs you have unresolved trauma. Please let us know your thoughts on unresolved childhood trauma in adults and your experience with healing by commenting down below!
Frequently Asked Questions
What happens to adults with unresolved childhood trauma?
Adults with unresolved childhood trauma might struggle with social interactions and forming meaningful connections with others, experience various health issues, grapple with low self-esteem, and feel a lack of direction in life.
How do you fix unhealed childhood trauma?
Recognizing the warning signs of unresolved trauma is the first step toward seeking help and finding healing. If you or someone you know is struggling with unresolved trauma and its effects, it’s important to reach out to a mental health professional or helpline in your country for assistance.
What are the long term effects of unresolved trauma?
Delayed responses to trauma can manifest in a variety of ways, including persistent fatigue, sleep disturbances, recurring nightmares, a constant fear of the trauma reoccurring, heightened anxiety triggered by flashbacks, feelings of depression, and a tendency to avoid emotions, sensations, or activities that remotely remind them of the traumatic experience.










Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.