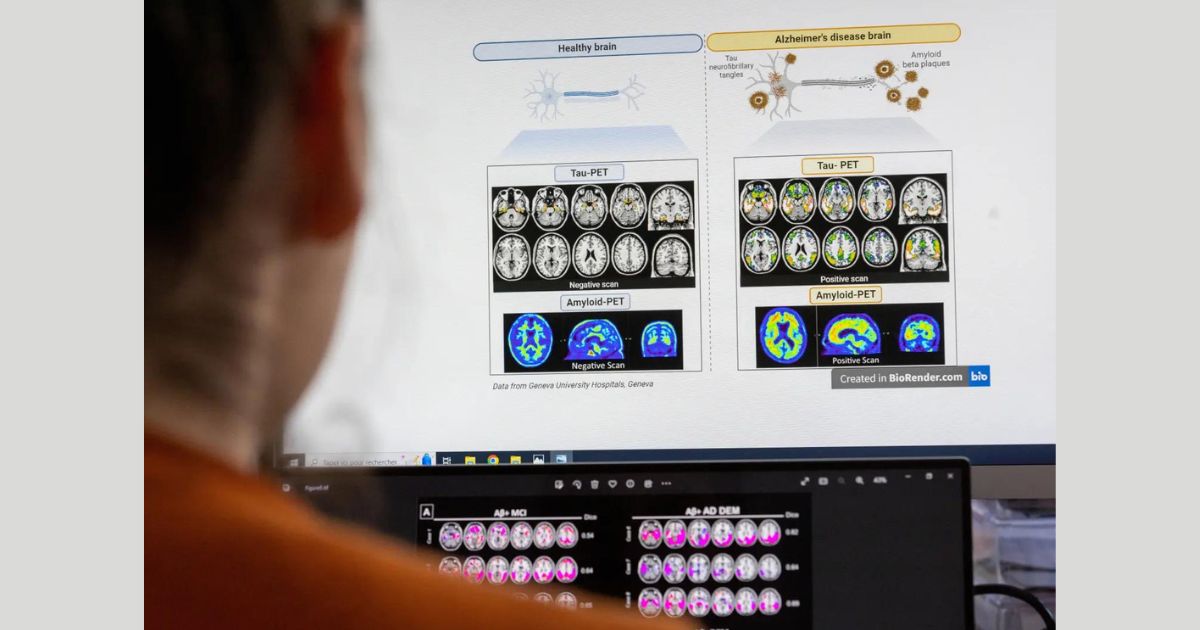
In a groundbreaking study, researchers from the U.K. and China have uncovered a potential breakthrough in the early detection of dementia. Published in the journal Nature Aging, the study analyzed frozen blood samples and identified a range of proteins that may predict various forms of dementia more than 10 years before clinical diagnosis.
The research, aimed at identifying individuals at risk for dementia using a simple blood test, represents a significant advancement in the field. While current methods rely on costly brain scans to detect abnormal protein levels associated with Alzheimer’s disease, this new approach offers a more accessible and cost-effective alternative.
Dr. Jian-Feng Feng of Fudan University in Shanghai, one of the study authors, emphasized the importance of such tests in aging populations, particularly in countries like China. Discussions are already underway for the potential commercial development of a blood test based on the research findings, highlighting its potential impact on global healthcare.
The study, conducted by researchers from the University of Warwick and Fudan University, analyzed over 52,000 blood samples collected between 2006 and 2010 from individuals without signs of dementia at the time. Of these samples, 1,417 individuals eventually developed Alzheimer’s disease, vascular dementia, or dementia from any cause.
Researchers identified 1,463 proteins associated with dementia and ranked them based on their predictive capabilities. Among the proteins, GFAP, NEFL, GDF15, and LTBP2 were consistently linked to higher risks of developing dementia. Individuals with elevated levels of these proteins were significantly more likely to develop dementia, providing valuable insights into potential biomarkers for early detection.
While the study results are promising, researchers acknowledge the need for independent validation of their findings. However, the identification of neurofilament light, a protein already used in clinical settings for certain conditions like multiple sclerosis, further validates the potential of blood-based biomarkers for dementia prediction.
Blood Test For Early Detection of Dementia
Dr. Suzanne Schindler, an Alzheimer’s researcher at Washington University in St. Louis, highlighted the significance of clinically available blood tests for Alzheimer’s disease, which could enhance the accuracy of dementia prediction. Such tests are already playing a crucial role in identifying candidates for clinical trials testing treatments in patients with early-stage or presymptomatic disease.
Overall, the study offers hope for early intervention and improved outcomes for individuals at risk of dementia. By leveraging blood-based biomarkers, healthcare professionals may soon be able to identify at-risk individuals years before symptoms appear, opening new possibilities for preventive interventions and personalized treatment approaches.







Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.