You can say a lot about a person and what they’re thinking from a few fleeting behaviors they might exhibit. In this article, we are going to talk about several fleeting behaviors and how you can understand so much just by looking at someone’s body language.
From the foot that suddenly orients toward the exit when we need to leave to the ventilating of a shirt when someone asks us a question we would rather not answer, our bodies are constantly communicating, even if we don’t realize it.
Feelings, desires, fears, even intentions are often expressed first by our bodies—often long before we speak our minds.
From the time we are born, our bodies constantly communicate needs, wants, discomfort, even desires (ask any parent of a new-born)—from the wiggling of our toes, to a furrowed forehead, to the dilated pupils and arched eyebrows that heartily welcome a mother into view.
Knowing that the entire body communicates can help us to decipher others. Recognizing which behaviors are more accurate or revealing is also helpful.
Pulling on our earlobe as we struggle to remember a password most everyone can figure out; but noting that your fingers have moved closer together—a sign of lack of confidence useful to a poker player or when deposing a witness—might not be as obvious.
Similarly, there are behaviors that are not just out of the way, discrete, or minute; they are also fleeting. They appear and disappear quickly and because they do, I call them tachykinesic behaviors, from the Greek tachys (fast) and kinisis (movement or behavior).
Related: 10 Body Language Cues That Can Instantly Give You Away
Tachykinesis* is particularly accurate because it occurs unfiltered—without the influence of the thinking brain (the neocortex). For example, before our thinking brain realizes someone stepped on our toes, we are already grimacing in pain, though it may be momentary.
These tachykinesic reactions, though transitory, reveal true sentiments precisely because they are so automatic. By their very nature, tachykinesic behaviors reveal information that the person performing them may not want us to know, especially if the individual is concealing fears, struggles, and anxieties or pretending to be cool under pressure.
The unveiling of true feelings or sentiments can give us an advantage in understanding what others are experiencing so that we can be more empathetic or discerning.
Recognizing the importance of tachykinesis in the study of nonverbal communications, I have put together a short list of some of the behaviors that help me to understand what people are thinking, feeling, or even concealing. (This is not a complete list; for that, see my book, What Every BODY is Saying.)
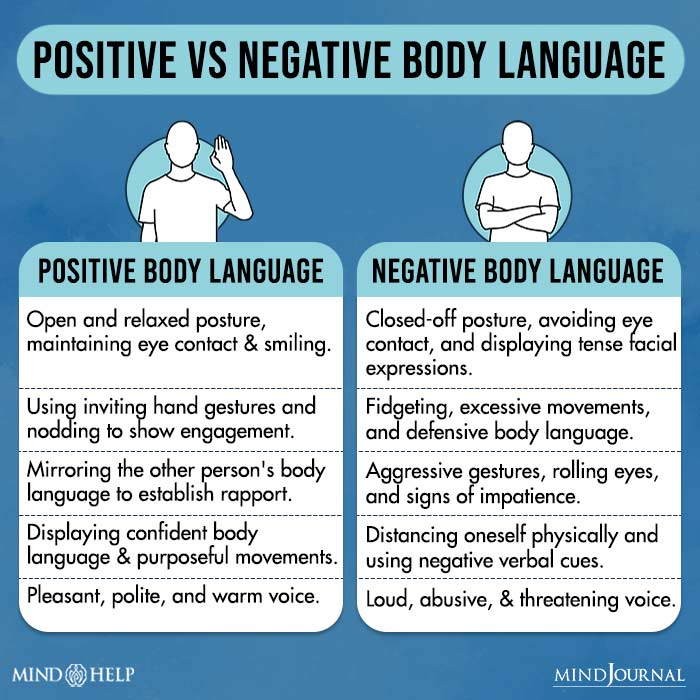
10 Fleeting Behaviors That Reveal So Much
1. Eyelid Flutter
Sudden eyelid flutter (1/300 of a second) suggests something is wrong or that a person is struggling with something they heard, saw, or are processing.
Often seen when people are struggling to find the right word to use or can’t believe what they just heard or witnessed.
2. Eye Twitch
Under high stress, the small muscles just under the eye and above the cheekbone will briefly twitch uncontrollably, signaling a high degree of psychological discomfort. (Even though “eye twitch” is a misnomer, it is often referred to by this name.)
This behavior is frequently observed when someone being interviewed fears the interviewer or is trying to suppress the fact that they are nervous.
3. Pupillary Constriction
Our pupils constrict when we see something we don’t like or when we have negative emotions. It’s obviously easier to detect in light-colored eyes, but nevertheless, when pupils suddenly constrict, something negative has transpired.
Interestingly, our brain governs this activity to make sure that our eyes are very focused as the smaller the aperture—the iris in this case, which surrounds the pupillary zone of the eye—the greater the clarity. Pupilary size can change in less than 1/500 of a second.
4. Squinting
Squinting is our way of displaying displeasure or concern, especially when we hear or see something we don’t like. With some people the response is so accurate that whenever they hear something they don’t like, they squint ever so briefly.
Having said that, keep in mind that we also squint our eyes when we are focusing on something or trying to make sense of something we have heard.
Related: 40+ Body Language Signs And Cues To Strip Down Someone’s Personality
5. Tongue Press
To relieve stress (usually significantly high stress) a person will quickly press the tongue against the inside of the mouth—noticeable through the cheeks. This is also seen in individuals caught doing something wrong. Because it’s vanishes quickly, it is easy to miss.
6. Lip Pull
This is similar to pursed lips (lips are puckered forward tightly), the big difference being that in this case, the pursed lips are dramatically pulled quickly to the side of the face significantly altering the look of the person.
Usually this happens in a dramatic instant, though some people will hold that position for a few seconds dramatically distorting their face. As an example, Olympic gymnast McKayla Maroney displayed pursed lips when she was displeased with her second-place finish at the London Olympics.
Lip pursing means I don’t like or I disagree; when pulled dramatically to the side, those sentiments are that much more intense, as we see here in Kato Kaelin, above, during the OJ Simpson trial.
7. Adam’s Apple Jump
When the Adam’s apple suddenly jolts upward (like bread in a toaster), chances are the person has just heard something that causes them to be very anxious or scared.
Extreme stress or anxiety is the culprit behind this behavior—and as dramatic as it appears, most people don’t realize when they do it.
8. Thumbs Up
Thumbs that suddenly pop up while fingers are interlaced indicates confidence in what is being said. Usually seen when the hands are on the lap or on top of a desk or table.
As the person genuinely emphasizes, the thumbs pop up like two exclamation points. Because conversations can be very fluid, this behavior is fleeting and temporary depending on the flow of the discussion.
9. Thumb Withdrawal
When we feel insecure or threatened, we withdraw our thumbs subconsciously and tuck them next to our fingers or even underneath the fingers. A sudden tucking in of the thumb means a person is concerned, anxious, worried, or threatened.
This is a survival tactic we have similar to what dogs do when they tuck their ears down because of fear or fright.
Related: The Power of Perception: Why Reading Emotional Expressions is Vital
10. Foot Kick
While sitting with one leg over the other, the person suddenly does a quick kick. This is different than the foot shaking that is often seen to relieve boredom.
The foot kick is more dramatic and usually follows something negative or contentious, or something they wish to avoid talking about.
These 10 easy-to-remember behaviors reveal what a person is experiencing in real time. They are accurate because they occur immediately, in real time, without conscious deliberation.
While the whole body communicates in different ways, tachykinesis is one more area of study to help us understand human communications and to decode what is truly in the heart and mind.
*Tachy is as at the root of words such as tachometer and tachycardia (fast heartbeat).
Want to know more about nonverbal communication and fleeting behaviors? Check this video out below!
Check out Joe Navarro’s website for more such informative and interesting articles. His books are available to purchase here.
Additional Reading Material
Haggard, E. A. and Isaacs, K.S. 1966. Micromomentary Facial Expressions. In Methods of Research in Psychology, L.A. Gottschalk and A.H. Auerback, Eds. New York: Appleton Century Crofts.
Navarro, Joe. 2008. What Every BODY Is Saying. New York: HarperCollins.
Porter, S., & ten Brinke, L. (2008). Reading between the lies: Identifying concealed and falsified emotions in universal facial expressions. Psychological Science, 19, 508-514.
Written By Joe Navarro M.A.
Originally Appeared On Psychology Today








Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.