Our emotions influence how we think, behave, act, and interact with others. This is why it is crucial to understand our basic emotions as it can help us gain better control over ourselves and live a more mindful life.
What are basic emotions
Humans experience a wide range of emotions that affect our decisions, perceptions, and actions. According to a research paper published in the American Psychological Association (APA), “basic emotions are often held to be the primitive building blocks of other, nonbasic emotions.”{1} Several psychologists have attempted to identify the various forms of human emotions. And as a result, multiple theories have been proposed to explain exactly what we feel.
The idea of primary or basic emotions can be traced back to the first-century Chinese encyclopedia known as the Book of Rites (Li Ji), {2, 3} according to a psychiatrist and award-winning author Neel Burton, M.D{4}. The book explains seven feelings experienced by humans, such as love, joy, liking, anger, sadness, fear, and disliking. However, in the 20th century, American psychologist Paul Ekman{5} recognized six basic emotions, which is widely accepted as the most common theory.
Related: Wheel of Emotions – The Perfect Tool To Better Understand Your Emotions
The primary human emotions pointed out by Ekman are:
- Happiness
- Sadness
- Fear
- Disgust
- Anger
- Surprise
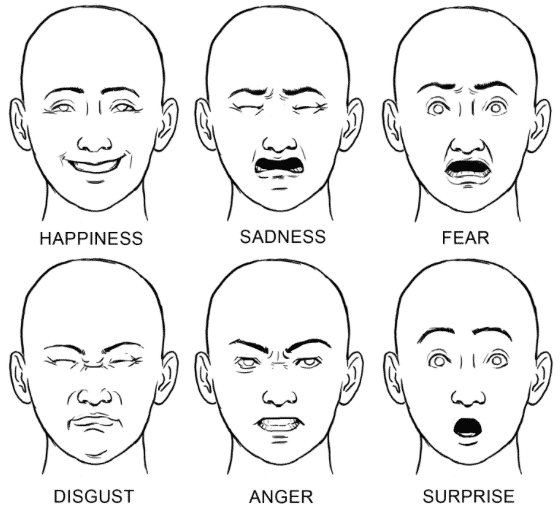
However, the list was later modified to consider shame, pride, excitement, and embarrassment as primary emotions. But it should be noted that recent research by Glasgow University{6} has found that there are four basic emotions instead of six. Another 2017 study{7} revealed that there are as many as 27 distinct categories of emotion along continuous gradients. This study was published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Although there are many other theories {8, 9} about how emotions influence the human experience, it is believed by most experts that Paul Ekman’s theory of six basic emotions{10} is one of the best.
Understanding 6 basic emotions
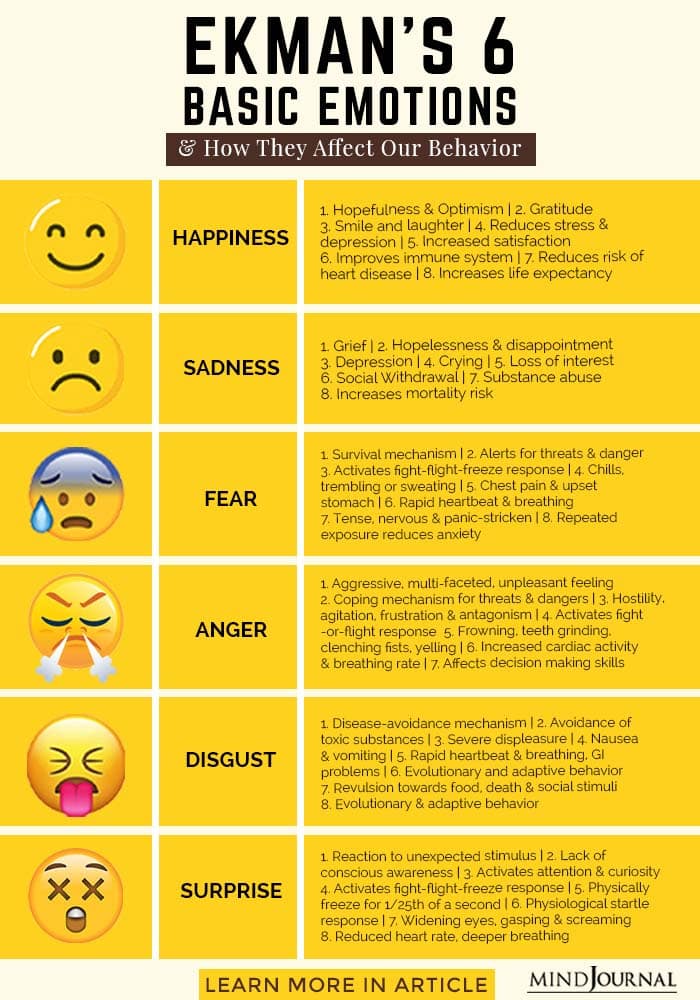
Here we are going to take a deeper look at the basic human emotions as identified by psychologist Paul Eckman and how they influence our behavior:
1. Happiness

All of us strive for happiness. It is defined as a pleasant mental and emotional state involving feelings of joy, satisfaction, contentment, gratification & wellbeing. Happiness is a reward for thoughts, actions, and behavior that benefits us.
Happiness is generally expressed in the following ways:
- Smiling, laughing and other similar subtle facial expressions
- Having a relaxed stance, clasping hands together, clenching fists
- Speaking in a pleasant manner and having an upbeat tone of voice
How it affects us:
Although happiness is considered as perhaps the most important primary emotion, what we believe will make us happy is often influenced by our friends, family, peers, and even pop culture. However, what actually makes us happy is more individualized and complex. Research shows that happiness can cause several health benefits.{11}
It can help to reduce stress, improve the immune system and reduce the risks of heart diseases. In fact, being happy can also increase our life expectancy, according to studies.{12}
2. Sadness
Happiness can not only increase our longevity but can also improve our relationships and boost marital satisfaction{13}. Unhappiness, on the other hand, is associated with a range of negative mental, emotional and physical health outcomes. Being unhappy can often lead to higher levels of loneliness, stress, anxiety, depression, and reduced life expectancy.

Despite how much we want to, we can never escape from sadness. Certain life experiences tend to make us feel sad and upset. In fact, it is one of the most damaging basic emotions as severe and prolonged sadness can lead to depression and suicidal tendencies.{14} It is primarily a short-lived emotional state marked by feelings of low mood, grief, disappointment, hopelessness, and disinterest.
Sadness is often characterized by the following:
- Crying and tears
- Frown
- Feeling hopeless
- Feeling lethargic
- Withdrawing from social interactions
- Loss of interest
- Quietness
- Being upset & dampened mood
Related: The 7 Physical Signs of Extreme Sadness
How it affects us:
The intensity and the type of this emotion mainly depend on the individual and the reason for the sadness, which can also influence one’s ability to deal with it. Extreme and prolonged sadness can make us look for certain coping mechanisms like self-medicating, avoiding others, thinking about a negative experience, and substance abuse.{15} However, such behaviors can be psychologically, emotionally, and physically damaging and lead to stronger feelings of sadness.
A 2008 study found that sadness is an integral part and a core symptom of depression. Another 2017 study revealed that depression can significantly augment mortality risk. The researchers state “The association between depression and mortality persists over long periods of time.” {16, 17}
3. Fear

It is an essential primary emotion that generates the fight or flight response and keeps us safe in times of danger and threat. Although it is considered a negative emotional state, fear is a survival mechanism for our safety and health.
According to a study {18} on fear, the amygdala, a bunch of cells near the brain’s base, identifies and regulates responses to natural threats and dangers. It is also related to the stimuli which predict the occurrence of danger. Fear is necessary for activating survival behavior in potentially life-threatening situations. It also enables us to learn defensive responses.
When we are experiencing a threat or danger, the amygdala expresses conditioned fear leading to the fight or flight response. This instinctive response makes sure that we are ready to cope with the existing danger effectively.
Fear is usually expressed in the following ways:
- Tense stretched lips, wide eyes and other facial expressions
- Heart beating faster & rapid breathing
- Running away, hiding or other similar body language
How it affects us:
However, certain individuals actively seek experiences that evoke feelings of fear like watching horror movies, extreme sports, and other fear-inducing activities. When we repeatedly expose ourselves to a situation or object we are afraid of, we can become familiar with it which reduces feelings of anxiety, panic, and fear.{19}
Certain physiological symptoms of fear show instant activation and preparation for mostly “flight” or even “freeze” than “fight”.{20} Our cardiac activity becomes intense, breathing becomes faster, irregular, shallow, and harder. However, the more we expose ourselves to controlled fear, the less fear starts to affect us.
This is why exposure therapy {21} is widely recommended to people with different phobias as it gradually exposes them to the feared object in a controlled and safe setting. The feeling of fear decreases eventually.
Related: Ways To Let Go OF Your Fears, Insecurities, and Negativities For A Fulfilling Life
4. Disgust

“Disgust is a strong and visceral emotion that can arouse powerful affective and behavioral responses” explains a 2011 study. {22} It is one of the basic emotions which we don’t usually consider as a primary feeling. However, it plays a crucial role in our lives. This refers to feelings of repulsion and avoidance of substances that we believe can be dangerous if ingested. It leads to feelings of severe displeasure and enhances activation in our bodies.
Disgust serves an evolutionary and adaptive purpose to reject and substances that could be contaminated or toxic. However, this specific emotion can be activated due to toxic social stimuli as well.
This is how we mostly express disgust:
- Turning away, frowning, curling or lips, wrinkling of nose etc
- Revulsion, nausea, vomiting
- Gastrointestinal problems, muscular tension
- Increased breathing rate and heart rate
How it affects us:
This primary emotion can occur due to several adverse experiences like a nasty and obnoxious smell, sight, or taste. Experts claim that disgust mainly evolved as an instinctive reaction to specific foods which can be poisonous or harmful.{23}
Moreover, unpleasant things like infection, poor hygiene, blood, and even death can make some people feel disgusted. In fact, according to research, disgust may be a disease-avoidance mechanism that protects us from falling sick. {24}
5. Anger

We feel angry when a certain situation makes us frustrated. Anger is an intense, unpleasant feeling that often prompts us to act without thinking. Anger can be an ambiguous and multi-faceted feeling which is usually not properly identified or justified. It is one of the most evolutionary beneficial emotions among the 6 basic emotions.
According to a 2017 study, anger is considered as one of the basic emotions, “mainly given its distinct and universally recognizable pattern of facial expression.” The study adds that anger can also hint at the presence of Narcissistic Personality Disorder (NPD). {25}
Anger enables us to cope with frustrating people and environments, threats, dangers, and challenges. It offers us certain resources that ensure we successfully overcome these. However, if anger is ineffective in helping us deal with frustrating situations, then we shift to feeling sadness.
It is an intense and dominating emotion marked by frustration, agitation, antagonism, and hostility towards others. Anger also plays a crucial part in our fight or flight response and is more associated with “fight” than “flight”.
We often express anger in the following ways:
- Glaring and frowning
- Tight lips, nose flaring, teeth grinding & jaw clenching
- Clenching fists and having a strong stance
- Shouting, yelling, speaking aggressively
- Punching, kicking, hitting or throwing items
How it affects us:
Anger can not only prepare us for action but also increase our cardiac activity. It can make the muscles tense and augment breathing rate. Moreover, it also boosts cognitive tension by increasing the production of adrenaline in the blood. However, when in control, anger can also be beneficial for us. It can encourage us to pursue our needs, find probable solutions and take necessary action.
However, when it is extreme, uncontrollable, or expressed in an unhealthy manner, it can be dangerous for self and others. When not regulated in time, it can lead to aggression, violence, and abuse. Anger can impact our decision-making skills and lead to health risk behaviors, according to a 2010 study. It can also cause diabetes and coronary heart diseases as well. {26}
Related: How You Can Manage Your Anger And Never Let It Control You
6. Surprise

Last but not the least, the surprise is one of the basic emotions {27} explained by psychologist Paul Eckman. It is a reaction to something unexpected and unprecedented. Surprise is a sense of astonishment, wonder, or amazement.{28} Researchers state that “surprise is an emotion arising from a mismatch between an expectation and what is actually observed or experienced.” It necessitates a mechanism for comparing reality with an expectation. {29}
It is often followed by a feeling of uncertainty and a lack of conscious awareness. This emotion compels our mind to clear all current working memory associated with residual activity so that we can deal with the unexpected stimulus.
Hence, it activates our attention as well as curiosity-related behavior. A surprise can be positive or negative and based on the experience it can make us feel joy or sadness respectively. Unlike other emotions, it typically lasts for a brief period of time and is marked by physiological startle response and anxiety.
Most of us tend to express our surprise in the following manners:
- Opening mouth, widening eyes & raising eyebrows
- Jumping and putting hands on chest
- Gasping and screaming
How it affects us:
When we are surprised, our heart rate decreases, and our muscular tone increases. Our breathing usually gets deeper, pitch increases and we tend to make impulsive vocalizations. Surprise can also activate the fight-flight-freeze response and release adrenaline to either face the situation, run away, or freeze in fear.
This cognitive-emotional phenomenon can significantly impact our behavior and decision-making as we generally observe surprising incidents disproportionately. {30}
Basic emotions are a survival mechanism
Studies show that emotions play a crucial role in our evolutionary development, survivability, and highest performance across all conditions. {31} Irrespective of whether an emotion is positive or negative, the main purpose of every emotion we experience as human beings are to ensure our survival.
However, when we are unable to control and manage our emotions, it can often translate into danger. This is why emotional regulation is crucial so that our thoughts, beliefs, and behavior are not dominated by our emotions.
Emotions allow us to live our lives the best way possible. When we understand the nuances and complexities of basic emotions, we can understand how our emotions define us and our behavior to create a life of depth and meaning.
Related: 8 Ways You Can Regulate Your Emotions
Here is an interesting video that you may like:
References:
1. https://doi.apa.org/doiLanding?doi=10.1037%2F0033-295X.97.3.315 2. https://www.amazon.com/Book-Rites-Liji-Bilingual-English-ebook/dp/B00KVGYS9M 3. https://books.google.co.in/books/about/The_Book_of_Rites_Li_Ji.html?id=De9qngEACAAJ&redir_esc=y 4. https://www.amazon.com/Neel-Burton/e/B001JS3ISI?geniuslink=true 5. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8512154/ 6. https://www.gla.ac.uk/news/archiveofnews/2014/february/headline_306019_en.html 7. https://www.pnas.org/content/114/38/E7900 8. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00781/full 9. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/318447136_Basic_Emotions 10. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2781895/ 12. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1322236/ 11. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3609702/ 13. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4158846/ 14. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3181878/ 15. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5654987/ 16. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7113180/ 17. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4864601/ 18. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9861466/ 19. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1299209/ 20. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4495877/ 21. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4125602/ 22. https://doi.apa.org/doiLanding?doi=10.1037%2Fa0014823 23. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3189359/ 24. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3013466/ 25. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3019061/ 26. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5681963/ 27. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31577880/ 28. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3858647/ 29. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30375159/ 30. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26330382/ 31. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5673219/











Leave a Reply