Are someone with an unhealthy relationship with your food? You might be surprised to know that childhood trauma and eating disorders might be related.
Those of us who had a troubled childhood plagued with abuse and trauma might be at a greater risk of developing eating disorders at a later period of our lives. Here, we have explained the complex correlation between childhood trauma and eating disorders, take a look.
Did you know that in the United States alone, millions of adults and young adults struggle with overeating and undereating disorders, such as Binge Eating Disorder or BED, Bulimia Nervosa, and Anorexia Nervosa?
If you are a woman, brace yourself for more bad news, as although trauma and eating disorders can be found in men, research suggests these unhealthy eating patterns are seen more in women.
So what causes eating disorders in adults? Well, there are several factors that can trigger unhealthy eating habits in a person, including genetics, family history, home environment, etc.
However, the most striking and one of the most common factors that link these cases of eating disorders is a history of adverse childhood experiences or childhood trauma.
Sadly, those who have experienced physical, emotional, or sexual abuse as a child, are at a greater risk of developing various psychological issues like poor body image and eating disorders.
Childhood Trauma And Eating Disorders: How Does Childhood Abuse Raise Risk?
Let’s now explore in detail how trauma and eating disorders are interlinked.
The Statistics
The relationship between childhood sexual abuse and eating disorders has been a matter of debate for quite some time now. According to a study, approximately 30% of all the patients with eating disorders have endured childhood sexual abuse.
Although correlation and causation are not the same, we have enough instances that compel us to examine the link between eating disorders and trauma from childhood experiences.
Types Of Trauma And Their Role In Development Of Eating Disorders
While analyzing the correlation between childhood trauma and eating disorders, you must not ignore that there are different forms of childhood trauma, other than sexual abuse, that can lead a person towards unhealthy eating habits.
Physical and emotional abuse suffered at a very young age can leave a person scarred for life. Children in their impressionable years are still learning to develop their self-identity and to form perceptions of those around them.
When a child is repeatedly exposed to trauma, be it physical, emotional, or sexual, the effects can be extremely damaging to their developing mind. It becomes difficult for the child or adolescent to process or regulate their emotions.
As a result, negative behaviors such as purging, binge eating, or undereating emerge and become coping mechanisms for the child. These unhealthy eating habits serve the following purposes:
- To have a sense of control when they feel they have none
- To distract themselves from the painful reality of their life
- To adopt a survival strategy and avoid the abuse
How Do Childhood Emotional Abuse Causes Eating Disorders?
Emotional abuse can be in different forms like continuous and harsh criticism, belittling or dismissive attitude, ignoring the emotional needs of a child, or any kind of emotional invalidation.
When children undergo these types of toxic treatment, they start internalizing the negative responses and start forming limiting ideas about themselves. They develop low self-esteem and believe that they are unlovable.
The barrage of insults and psychological attacks leads them to develop self-critical views and body image issues, which manifest through eating psychopathology.
Children who grew up with emotional abuse might exhibit dysfunctional behaviors, such as acting out impulsively, something associated with bulimia nervosa, or they can get emotionally restricted and detached, a behavior commonly linked with anorexia nervosa.
Let’s Look At The Effects Of Emotional Abuse At A Glance:
- Lack or low tolerance to negative feedback and distress
- Stunted emotional development
- Emotional inhibitions
- Body image issues
- Self-critical views
- Poor self-esteem
Read: Eight Mental Abuse Tactics To Watch Out For
How Does Childhood Sexual Abuse Cause Eating Disorders?
Several risk factors like the inherent issues of self-control, types of trauma, etc., make it challenging to establish the causation between childhood sexual abuse trauma and eating disorders in later life. However, research indicates that there is a strong connection between the two.
It can be argued that people who suffered sexual abuse in their childhood resort to dysfunctional eating behaviors for the following purposes:
- A coping mechanism
- An outlet to channel their pain
- A measure to change their physical appearance and to ward off sexual predation
Eating Disorders And PTSD

As you have seen by now how childhood trauma and eating disorders can be correlated, you must also take note of the prevalence of eating disorders in patients struggling with PTSD or Post Traumatic Stress Disorder, as the psychological ramifications of repeated childhood abuse.
A study proves that individuals with experiences of childhood maltreatment commonly display symptoms of eating disorders as well as PTSD.
Eating Disorders In Women
As we have mentioned earlier, women bear the brunt of childhood trauma and eating disorders more than men. Also, according to research, childhood trauma and binge eating are more common in women than other forms of eating disorders.
Purging and other compensatory behaviors involved in Bulimia Nervosa are also commonly associated with childhood abuse, among women.
Hence, it can be said that women with adverse childhood experiences are more likely to develop Bulimia Nervosa, proving a strong commonality between childhood trauma and overeating.
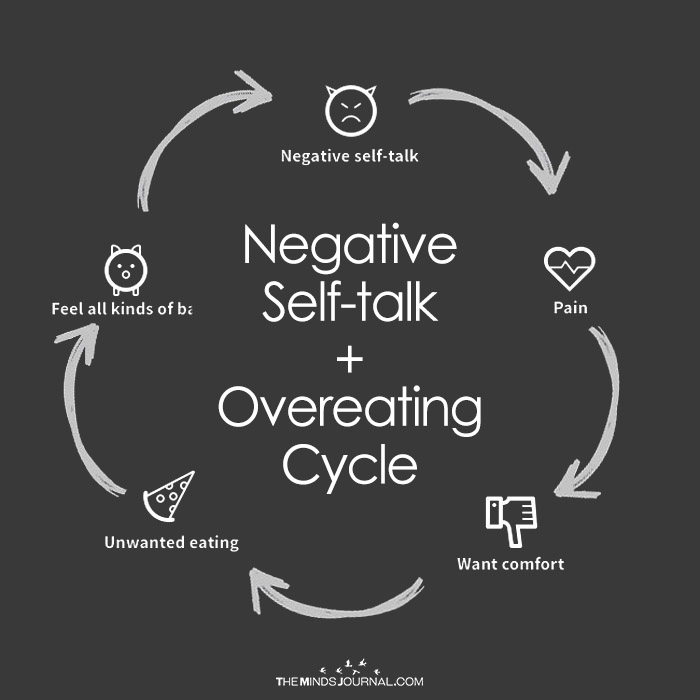
What Are The Effects Of Untreated Eating Disorders On Health?
Eating disorders if left unchecked can adversely affect our physical and mental health in the below-given ways:
Effects On Physical Health
- Malnourishment
- Obesity
- Infertility
- Altered Menstrual Functioning
- Osteoporosis
- Esophageal Cancer due to Purging
- Nutrients deficiency
- Gestational Diabetes
Effects On Mental Health
Read: Core Wounds: 12 Signs You Have an Unhealed Core Wound

Healing Childhood Trauma And Treating Eating Disorders
While treating a person suffering from both childhood trauma and eating disorders, a holistic approach is needed, including the need for proper nourishment, psychological counseling, addiction rehabilitation, and other related factors.
The following treatment options can prove to be helpful:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
- Dialectical Behavioral Therapy
- Inpatient Treatment
- Peer Support Group
You Are Not What Happened To You
Breaking free from a toxic and hurtful past is not as easy as it may seem, but if you or someone you know are struggling with trauma and binge eating, or any other kind of eating disorder, know that it is possible to leave the past behind and to adopt a healthier way of living.
Talking to a mental health professional or joining a support group can bring a significant change in the perception of a person struggling with an eating disorder.
Read: 7 Behaviors Common Among Adults Who Went Through Trauma At A Young Age
If you find our article on childhood trauma and eating disorders to be helpful, don’t forget to comment below and let us know. Also, feel free to share your experience regarding trauma and overeating, or any other dysfunctional eating behavior.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a food trauma?
Food trauma is a psychological condition that occurs when you consume specific types of food associated with a negative experience or a traumatic past.
What causes eating disorders?
There are several factors that can trigger unhealthy eating habits in a person, including genetics, home environment, etc. However, the most common factor is the history of adverse childhood experiences













Leave a Reply