Do you react instinctively in stressful situations? This is our fight or flight response in action. But what does fight or flight response mean? How does it affect our bodies and minds in moments of danger or stress? Let’s find out.
Have you ever wondered why your heart races, your palms become sweaty, and your muscles tense up when faced with a threatening situation? It’s as if your body has an automatic switch that activates a primal instinct to either fight or flee.
This remarkable response is known as the fight or flight response, and it plays a crucial role in helping us survive dangerous situations. Today, let us explore what does fight or flight response mean, symptoms of fight or flight response, what causes a fight or flight response and how to get out of fight or flight mode so that you don’t get stuck.
What Does Fight or Flight Response Mean?
The fight or flight response is an innate physiological reaction that prepares our bodies to confront or escape from perceived threats or dangers. When triggered, this response triggers a cascade of physiological changes in our bodies, enabling us to react swiftly and decisively.
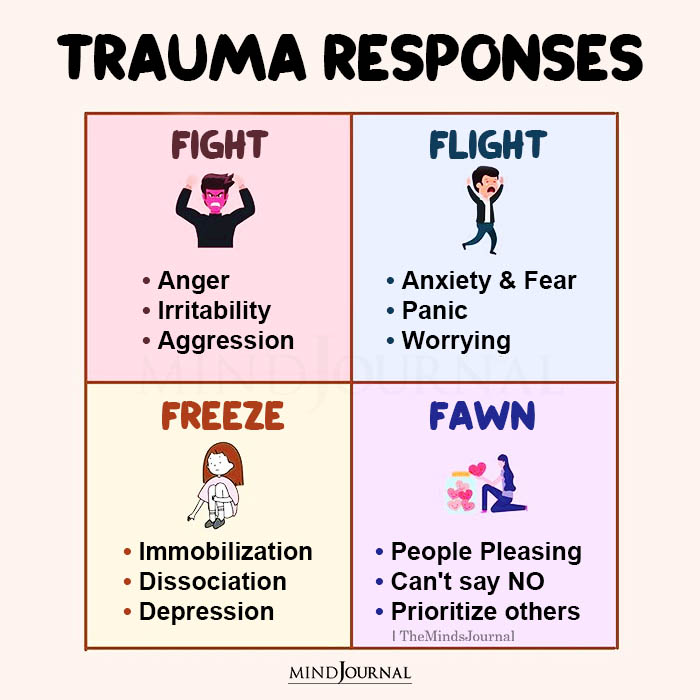
So exactly what does fight or flight response mean? According to researchers, psychological or environmental stress can often activate a surge of stress hormones that prepare us for action by producing physiological changes.
This activation of the sympathetic nervous system triggers an acute stress response, which is known as the “fight or flight” response. It’s nature’s way of getting us ready to face the challenge ahead.
It is a survival mechanism deeply ingrained in our evolutionary history, enabling our ancestors to respond quickly to life-threatening situations, such as encountering a predator in the wild.
Related: 5 Common Ways People Respond To Stress: Whats Your Stress Response Style?
Symptoms of the Fight or Flight Response
When the fight or flight response is activated, our bodies undergo a series of noticeable changes. These symptoms are the result of physiological adaptations designed to prepare us for immediate action. Here are some of the most common symptoms of fight or flight response –
1. Increased Heart Rate
One of the most noticeable symptoms is an accelerated heart rate. This occurs as the body pumps more blood to the muscles and organs, supplying them with oxygen and nutrients necessary for quick and efficient movement.
2. Rapid Breathing
Breathing becomes faster and shallower during the fight or flight response. This allows for a greater intake of oxygen, which is vital for providing energy to the muscles and enhancing alertness.
3. Heightened Senses
The fight or flight response sharpens our senses, making us more alert to potential threats. Our vision becomes more focused, and our pupils dilate to allow more light in, improving our ability to see in dim or threatening environments.
Our hearing becomes more acute, allowing us to detect faint sounds or danger signals.
4. Muscle Tension
The body prepares for action by tensing the muscles, readying them for a fight or a quick escape. This muscle tension can lead to sensations of stiffness, trembling, or even muscle cramps.
5. Sweating
As part of the fight or flight response, the body perspires to regulate body temperature and cool down in anticipation of physical exertion. Sweating can contribute to clammy hands, increased body odor, and a flushed appearance.

6. Surge of Adrenaline
The release of adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hallmark of the fight or flight response. Adrenaline triggers a boost in energy, increases blood flow to the muscles, and heightens mental alertness. This is one of the basic symptoms of fight or flight response.
7. Digestive Changes
During fight or flight, digestion slows down as blood is diverted away from the digestive system and toward the muscles and organs involved in the response. This can lead to symptoms such as a dry mouth, nausea, or a loss of appetite.
8. Cognitive Changes
The fight or flight response can impact our cognitive abilities. We may experience difficulty focusing on complex tasks, have racing thoughts, or find it challenging to make decisions due to the increased arousal and prioritization of survival-related processes.
Related: The 5 Most Common Trauma Responses: Beyond Flight or Fright
Now that we know what does fight or flight response mean and what symptoms of fight or flight response we should watch out for, let’s take a look at what causes a fight or flight response.
What Causes a Fight or Flight Response?
The fight or flight response can be triggered by various situations and stimuli. While it evolved to respond to immediate physical threats, it can also be activated by psychological or emotional stressors. Here are some common triggers:
1. Physical Threats
Facing a physical threat, such as encountering a dangerous animal or being involved in a physical altercation, can trigger the fight or flight response. Here the body prepares to defend itself or flee from the threat.
2. Psychological Stress
The fight or flight response can also be activated by psychological stressors, such as financial difficulties, relationship problems, or work-related pressure. Although these stressors may not pose an immediate physical danger, they can still trigger the same physiological response.
3. Emotional Stress
Intense emotions like fear, anger, or anxiety can activate the fight or flight response. This can occur in response to a traumatic event, a phobia, or even anticipation of a stressful situation.
4. Perceived Threats
The fight or flight response can be triggered by perceived threats that may not be objectively dangerous. Our brains are wired to assess and respond to potential dangers, even if they are not immediate or tangible.
This can include public speaking, performance evaluations, or social situations that trigger feelings of vulnerability.
5. Chronic Stress
Prolonged exposure to stress can keep the fight or flight response activated for extended periods. Chronic stressors, such as ongoing work pressure, financial instability, or relationship difficulties, can lead to an overactive stress response, negatively impacting both physical and mental health.
Understanding the symptoms and causes of the fight or flight response can help us recognize when it is activated and take appropriate steps to manage its impact effectively.

Knowing about what does fight or flight response mean and what causes a fight or flight response is not enough, we must also understand how to get out of fight or flight mode. Let’s take a look.
Related: How Stress Turns Us Into Someone Else: Your Stressed Self vs Your Best Self
How to Get Out of Fight or Flight Mode: 9 Tips to Break Free
While the fight or flight response is a valuable survival mechanism, prolonged periods of activation can have detrimental effects on our physical and mental well-being. To regain control and restore balance, it is essential to employ strategies that promote relaxation and calmness.
Here are some effective techniques on how to get out of fight or flight mode –
1. Relaxation Techniques
Engaging in relaxation techniques can help activate the body’s relaxation response, counteracting the fight or flight response. Techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, yoga, or listening to calming music can induce a state of relaxation and promote a sense of calmness.
Taking slow, deep breaths stimulates the vagus nerve, which activates the parasympathetic nervous system, counteracting the fight or flight response. Practicing mindfulness and meditation can help redirect our attention away from perceived threats and cultivate a sense of calmness and present moment awareness.
2. Self-Care
Prioritizing self-care is essential for managing the fight or flight response. Engage in activities that bring you joy and relaxation, such as hobbies, spending time in nature, or practicing self-compassion. Take care of your physical health by getting enough sleep, eating a balanced diet, and engaging in regular exercise.
3. Physical Exercise
Engaging in regular physical exercise not only helps burn off excess adrenaline and stress hormones but also promotes the release of endorphins, the body’s natural mood-elevating chemicals.
4. Cognitive Reframing
The fight or flight response is often triggered by negative thoughts and perceptions. Cognitive reframing involves challenging and replacing negative thoughts with more positive and realistic ones.
By reframing your thoughts, you can shift your perspective and reduce the perceived threat, ultimately calming the fight or flight response. Practice positive self-talk and challenge catastrophic or exaggerated thinking patterns.
Challenging and reframing negative thoughts and beliefs can help shift our perception of threats, reducing the frequency and intensity of the fight or flight response. This is how to get out of fight or flight mode.
5. Social Support
Seeking support from loved ones or participating in group activities can have a soothing effect on our nervous system, reducing the intensity of the fight or flight response.
6. Grounding Techniques
Grounding techniques involve redirecting your focus to the present moment and your immediate surroundings. This can help shift your attention away from perceived threats and reduce the intensity of the fight or flight response.
Examples of grounding techniques include focusing on your breath, engaging your senses by touching or feeling objects around you, or describing your environment in detail.

7. Emotional Regulation
Emotions play a significant role in activating the fight or flight response. Learning to regulate your emotions can help prevent prolonged activation of this response.
Techniques such as deep breathing, journaling, or talking to a trusted friend or therapist can assist in identifying and processing your emotions in a healthy way.
8. Create a Safe Environment
Creating a safe and supportive environment can help reduce the likelihood of triggering the fight or flight response. Surround yourself with people who make you feel secure and build a physical and emotional space that promotes relaxation and well-being.
Clear clutter, create a calming atmosphere with soothing scents or colors, and establish healthy boundaries in your relationships.
9. Seek Professional Support
If you find it challenging to manage the fight or flight response on your own or if it significantly impacts your daily life, consider seeking professional support. A therapist or counselor can provide guidance, teach you coping strategies, and help you navigate through underlying issues that contribute to an overactive stress response.
Remember, overcoming the fight or flight response requires practice and patience. Implementing these techniques consistently and adapting them to your unique needs can help you regain control, reduce stress, and cultivate a greater sense of calmness and well-being in your life.
Related: Stress: How It Affects The Mind And Body
Takeaway
So what does fight or flight response mean? The fight or flight response is a remarkable and vital part of our survival mechanism. By understanding its meaning, recognizing its symptoms, and exploring effective techniques to manage and reduce its impact, we can navigate the challenges of modern life with greater resilience and composure.
Remember, while the fight or flight response is automatic, we have the power to regain control and restore balance through conscious effort and self-care. So take a deep breath, embrace your inner strength, and face life’s challenges with a calm and grounded mindset.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
How do I turn off fight-or-flight response?
Manage fight-or-flight response with deep breathing, mindfulness, and relaxation techniques to calm the nervous system.
Can your body get stuck in fight-or-flight mode?
Prolonged stress can trap your body in fight-or-flight mode, but practices like meditation can help reset it.
How do you fix constant fight-or-flight?
Combat constant fight-or-flight by prioritizing self-care, seeking support, and practicing stress-reduction techniques consistently.










Leave a Reply