Are you intrigued by the nature of time and reality? If so, the concept of eternalism philosophy may fascinate you. This controversial view of time challenges our traditional understanding of past, present, and future, and offers a new perspective on the nature of reality.
The philosophy of time and space
What is time? Time is a concept that has fascinated and perplexed humans for centuries. We experience time every day, yet it remains an elusive and mysterious concept.
Time seems simple at first glance but raises complex questions. Philosophers have grappled with the nature of time for centuries, and there are many different philosophical perspectives on what time is and how it works.
Today we are going to explore the concept of eternalism, which is one of the most intriguing and controversial theories of time.
Related: Understanding Deja Vu: The Mystery of Time Explained

What is eternalism philosophy?
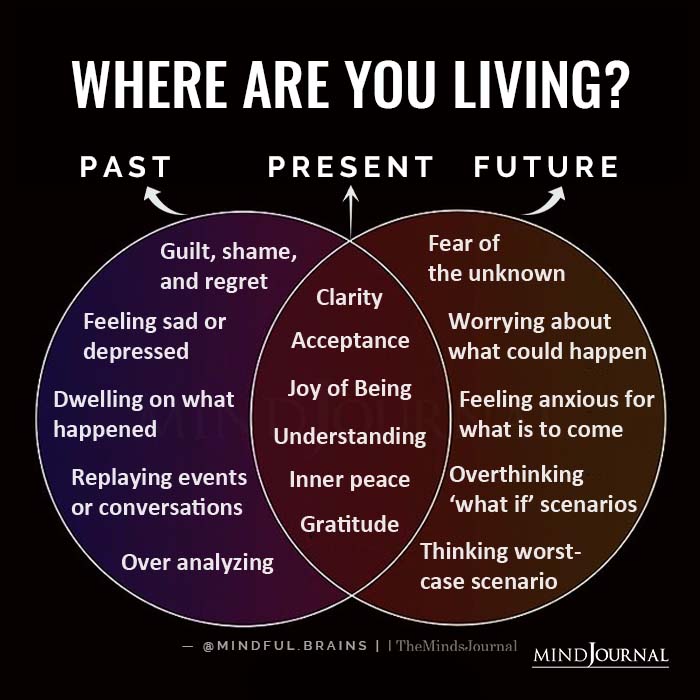
Eternalism, also called the Block Universe theory or B-theory of time, is the view that time is a dimension that exists independently of human consciousness. This means that past, present, and future events all exist simultaneously and eternally and are equally real.
In other words, time is like a landscape, where all events are spread out and can be accessed from any point in time. This perspective is in contrast to the more common view of time, which is called presentism, which holds that only the present exists, and the past and future are just mental constructs.
One way to understand what is time and eternalism is to think of time as a block universe. The block universe view suggests that time is like a solid block of spacetime, where all events, past, present, and future, are already fixed in place.
This view sees time as an unchanging whole, where every event is equally real and equally present. From this perspective, time is not something that flows or moves, but rather something that is static and unchanging.
Implications of eternalism philosophy
Eternalism or block universe theory has significant implications for our understanding of reality. If all events are equally real and equally present, then the distinction between past, present, and future becomes arbitrary.
This means that the idea of causation becomes more complex. If future events already exist, then it is difficult to conceive of a cause and effect relationship between events. Instead, events may be related in a more complex and interconnected way.
Eternalism philosophy also challenges our intuition about the nature of time. We experience time as a linear progression, where the past is fixed and unchangeable, the present is fleeting, and the future is uncertain.
This view of time is deeply ingrained in our everyday experience, and it can be challenging to reconcile with the idea that all events are equally present and real.
Debate around eternalism
Eternalism is a controversial view of time, and it is not universally accepted among philosophers. Some philosophers argue that eternalism is incompatible with our everyday experience of time.
They argue that we experience time as a flow, where events come and go, and the future is uncertain. From this perspective, time cannot be a static and unchanging whole.
Others argue that eternalism is the most logical and consistent view of time. They point out that the block universe view is supported by modern physics, which suggests that time is just another dimension.
From this perspective, time is no different from space, and all events are equally real and equally present.
Related: How To Find Happiness By Living In The Present Moment

Criticisms of eternalism philosophy of time and space
Here are some key criticisms of the eternalism philosophy of time:
1. It’s counterintuitive
Many critics argue that eternalism or block universe theory goes against our basic intuition that the future is open and undetermined, and the past and present are real whereas the future is not yet real. Eternalism claims all times are equally real, which seems bizarre and implausible to many people.
2. It undermines agency
If the future is already fixed, it appears to leave no room for genuine choice or agency. Our actions may feel free and undetermined, but on an eternalist view they are already decided. This threatens to undermine the very idea of free will.
3. It struggles to explain change
If all times already exist, it’s unclear how real change and temporal becoming are possible. Eternalists try to explain change in terms of states within the spacetime block, but critics argue this fails to account for the genuine dynamism we see in the world.
4. The “block universe” analogy is limited
While the block universe analogy can help explain some aspects of eternalism, it also has its limitations. Critics argue it doesn’t fully capture the experience of time or the role of experience and consciousness in shaping our perception of time.
5. It’s not empirically testable
Unlike scientific theories, eternalism cannot be tested through experiment or observation. It remains a purely philosophical theory with no way to conclusively prove or disprove it. This has led some critics to argue that eternalism is ultimately a meaningless and unfalsifiable hypothesis.
While eternalism offers a novel and interesting theory of time, a lack of empirical testability have led many philosophers to ultimately reject the view.
Eternalism & our understanding of the present
From an eternalist perspective, the present moment is just one of many equally real and equally present moments. This means that the present moment is not privileged over any other moment in time, and there is no fundamental difference between the past, present, and future.
This philosophy of time and space can be a challenging idea to wrap our heads around because we experience time as a linear progression, where the present moment is constantly changing and moving into the past. From this perspective, the present moment is special because it is the only moment that is real and immediately accessible to us.
However, from an eternalist perspective, the present moment is just one moment among many, and it has no special status or significance. This means that the distinction between the past, present, and future is arbitrary, and all moments are equally real and equally present.
This view of time has significant implications for our understanding of the present moment. If all moments are equally real and equally present, then the present moment is not a special or privileged moment in time. Instead, it is just one moment among many, and its significance is determined by its relationship to other moments in time.
From this perspective, the present moment is not an isolated or self-contained moment in time, but rather a part of a larger, interconnected whole. This perspective offers a new way of thinking about time and raises many intriguing questions about the nature of reality.
Takeaway
Eternalism philosophy is a fascinating and controversial view of what is time. It challenges our intuition about the nature of time and has significant implications for our understanding of reality.
While it is not universally accepted among philosophers, it provides a compelling alternative to more traditional views of time, such as presentism. By understanding eternalism, we can gain new insights into the nature of time and the world around us.
Related: Here Is Your Reminder That Growth Takes Time









Leave a Reply