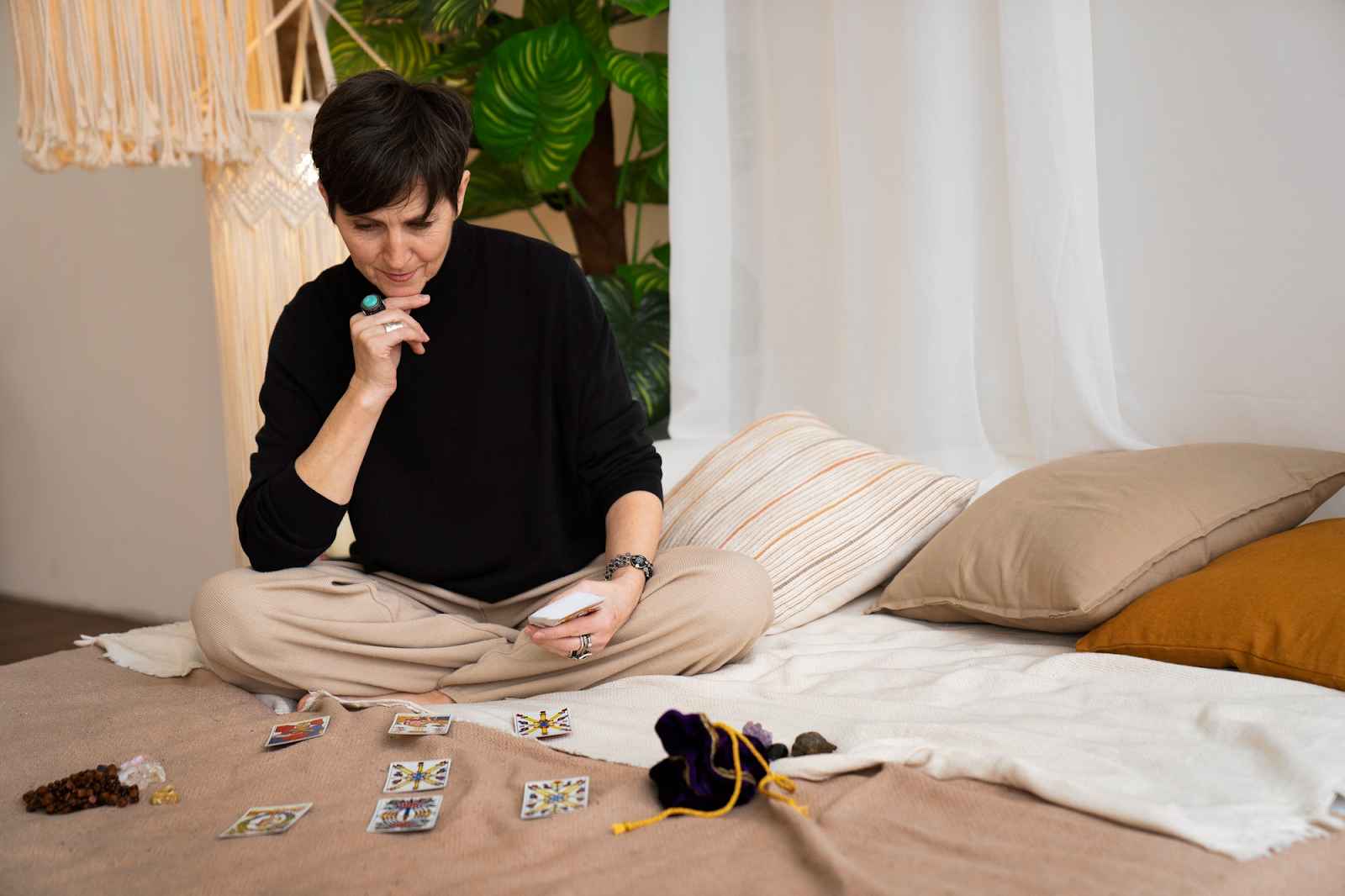
Mornings set the tone for the entire day. Many people wake up rushing, checking their phones, and moving through tasks on autopilot. A different start can change everything. Creating a moment of pause allows space to breathe, reflect, and step into the day with clarity. Tarot cards can provide that pause, offering a gentle way to reflect before the noise of life takes over.
Each card reveals imagery that stirs thoughts and emotions. Drawing a card in the morning sparks questions rather than answers. What stands out? What resonates today? This daily ritual encourages reflection, grounding, and intention, turning mornings into mindful beginnings.
Why Tarot Works as a Reflective Morning Tool
Tarot cards capture universal symbols that connect easily with personal experiences. A single image can stir memories, highlight emotions, or raise questions that might remain hidden during a busy morning. When you pause to look closely at a card, you invite the subconscious to surface and give shape to what you are carrying into the day.
The practice helps you shift away from prediction and toward awareness. It does not lock you into outcomes. Instead, the imagery offers prompts that you can interpret in ways that make sense for your life. This process fosters self-discovery and encourages mindful presence.
Some readers like to expand their practice with digital tools. Exploring an AI tarot reading tool can offer different interpretations, sparking new perspectives that might not arise on their own. This blend of tradition and modern insight makes daily reflection accessible, flexible, and deeply personal.
Setting the Morning Space
The environment you create shapes the quality of your reflection. Begin with a calm morning meditation corner where distractions are minimal. A small table, soft light, and a comfortable seat are enough to set the tone. Adding a candle or incense can deepen the sense of ritual, signaling that this time is set aside for stillness.
Choose a tarot deck that resonates with you visually. Keep a journal nearby so you can capture insights as they arise. Writing even a few sentences grounds your thoughts and helps reveal patterns that emerge over time. Consistency makes the practice meaningful.
This space acts as a gentle cue each day to pause and focus inward. It does not need to be elaborate. What matters is that it supports your intention to start mornings with clarity, reflection, and mindful connection.
Drawing a Daily Card
Starting the day with a single card creates a simple yet powerful ritual. Shuffle the deck slowly, letting your thoughts settle. Focus on the present moment rather than searching for specific answers. When you draw a card, treat it as a mirror, reflecting energy or emotions you might not notice otherwise.
For beginners, a one-card draw is the best option. It offers a clear symbol to reflect on without overwhelming you with interpretation. More experienced readers may enjoy pulling two cards: one highlighting the mood you carry into the day, and another guiding your intention forward.
Trust your instincts when selecting a card. There is no wrong choice because the meaning emerges through your interpretation. What matters most is allowing the imagery to spark reflection.
Reading the Card Mindfully
When you turn over a card, pause before reaching for guidebooks. Look carefully at the image. Notice the colors, the figures, and the symbols. Let your first impressions surface, even if they seem unclear. This moment of observation allows intuition to speak, offering insight that is personal and immediate.
Use questions to deepen reflection. Ask yourself what stands out today. Consider what the imagery might reveal about your current state of mind. Journaling even a few sentences captures these impressions, helping you see connections between the card and your daily experiences. Writing makes the reflection tangible.
Avoid chasing a single fixed meaning. The card serves as a prompt, not a rule. By staying open, you give yourself space to discover patterns and lessons that fit your life. This mindful way of reading turns tarot into a practical tool for daily self-awareness and growth.
Turning Reflection into Daily Intention
Reflection alone has power, but channeling it into a clear intention brings lasting impact. After considering the card, translate your insight into a short statement you can carry through the day. Keep it simple and positive. A phrase such as “I will listen with patience” or “I choose clarity in my actions” provides direction without pressure.
Writing your intention in a journal helps anchor it. Some people like to place the card next to their desk or carry it in a bag as a visual reminder. These small cues reconnect you to the morning reflection whenever distractions arise.
The value lies in repetition. When you practice setting intentions daily, the act shapes awareness and strengthens self-discipline. Over time, this habit builds resilience and balance, showing how a single tarot card can become a steady guide for mindful living.
Evening Reflection
Closing the day with the same card you drew in the morning completes the cycle of mindfulness. Take a few minutes to sit quietly and revisit the image. Notice how your understanding of it may have shifted after the events of the day. This second look often brings insights you could not see in the morning.
Journaling at night deepens the process. Write a sentence or two about how the card connected with your experiences. Did it highlight a challenge, guide your mood, or affirm a choice you made? Recording these observations builds awareness over time.
This gentle practice ties the day together. Morning reflection sets an intention, while evening review shows how that intention unfolded. With consistency, the cycle strengthens self-awareness, helping you approach each new day with a clearer sense of growth and personal direction.
Wrapping Up
Mindful mornings gain depth when tarot becomes a reflective prompt. A card drawn at sunrise does more than offer symbols; it opens a dialogue with yourself. Each image invites awareness, clarity, and a chance to set intention before the day unfolds. Treat this ritual as a gift of presence. Over time, these mindful beginnings create stronger balance, guiding you toward days shaped by reflection instead of reaction.









Leave a Comment