Do men and women cry in the same way? Is crying the same across cultures? Does crying really make you feel better? Is there any difference in the way infants and adults cry? Can a hard-hearted person cry? If you are trying to find answers to these questions, then it is time to know these amazing, scientific facts about crying backed by research.
Here are interesting facts about crying:
1. Common reasons for emotional crying.
- Loss – We cry for the loss of loved ones or money or any other precious thing in life.
- Happiness – We shed tears of joy when happy.
- Helplessness, physical pain, and discomfort – Crying because of injury in your leg or any other body part, or maybe you have hit the rock bottom and don’t know what to do.
- Empathic crying – Where you cry in response to the emotional reaction of someone else. For instance, you are crying with your bae who has lost his pet.
- Extraordinarily positive or moving situations – We cry when we experience something very positive in life like – meeting life goals and ambitions, holding your newborn in your arms, or any other moving situation.

Related: 35+ Mind-Bending Psychology Facts About Human Behavior
2. Gender and culture differences in crying.
Research on the relationship of gender roles and beliefs to crying highlighted that women cry more frequently and are prone to both positive and negative crying experiences across cultures. Unlike Asian and East African countries, women in Western countries are found to have higher frequencies of crying.
Check out the following facts about crying and how they differ gender-wise:
- Women cry 2 to 5 times per month while men cry 0 to 1 times per month.
- Women cry for a longer (for six minutes on average) duration than men (four minutes).
- During serious situations like death, it is likely to make both men and women cry.
- In 6% of cases, a man’s crying will become sobbing as compared to 65% of the time for women.
This sex difference in adults in regards to crying can be attributed to gender stereotypes. There are many cultures across the world where gender differentiation for emotional expression is pronounced.
Mostly boys grow up learning “boys don’t cry” and develop the habit of bottling their emotions. Men are socialized to believe that crying is a weakness, particularly in social situations. That said, male and female infants don’t show any differences in crying.
The gender differences in crying could also be because women are exposed to more emotional situations (like watching a melodramatic TV show) than men who are more into sports and similar stuff. The kind of movies men and women prefer to watch, books they like to read, and the music they listen to can all influence whether men and women will react with tears or not.

Wealth determines crying abilities too!
Researchers showed evidence of people in wealthy democratic countries crying more often than those in other countries. This is one of the fun facts about crying!
Read: 8 Science-Backed Benefits of Crying
3. Attachment style determines crying behavior.
One of the lesser-known facts about crying! In an international journal Social Behavior and Personality, participants with dismissive attachment style, preoccupied attachment, and fearful attachment style cried less and showed mostly negative emotions while crying. Whereas, those with a secure attachment style mostly cried over positive emotions and showed higher frequencies of crying.
4. Personality is related to crying too.
Literature on the scientific facts about crying revealed that –
- Empathetic people cry more both in positive and negative situations, than people with less empathy.
- Neurotic people cry more in negative situations than less neurotic people.
But, they show no differences in positive situations. However, both anxious and neurotic people tend to cry more frequently and easily than others. Extroverts cry more during negative situations and are less likely to shed “happy tears”.
Also, people who allow themselves to cry have better emotional intelligence than those who don’t cry. People with less emotional quotient cry less because they are not in touch with their feelings and don’t assess or respond to them. Therefore, they have more repressed feelings than those with a high emotional quotient. People with high emotional intelligence can better process their feelings.
Related: Emotional intelligence test
5. Crying changes our perspective.
When we see someone crying it affects our perception of that person according to the study published in the Journal Cognition and Emotion. One of the psychological facts about crying is that some people view the crying individual as emotionally weak and less aggressive.
On the other hand, some think that people who cry are reliable, empathetic, and sincere. The study also found Indirect support for the idea that crying is an attachment behavior designed to elicit empathy and support in others.
When we see someone crying, the same neuronal areas of the brain are activated when we cry ourselves. According to scientists human beings have evolved to the point where crying automatically triggers empathy and compassion in other people. In short, crying fosters bonding and connection with people.

Fun facts about crying: The place of crying also plays an important role:
An individual crying in the workplace is perceived as negative, but not when the person is crying in a personal or private setting.
6. Crying changes mood.

A “good” cry can make you feel better, while a “bad” cry can make you feel worse.
Some people cry to release their pent-up emotions, pain, or tensions. Does crying really make you feel better? That depends on the situation, with whom you are crying, and when you are crying.
Based on “good” and “bad” crying patterns that emerged from an international study including 5000 men and women, psychologists revealed the following crying facts –
- If you get support and comfort, when you are crying, then you are highly likely to feel better.
- People feel better after crying if they came to a happy realization about a situation.
- People feel better after crying if they gained a new perspective or understanding of a situation that caused tension.
- People feel better after crying if they came to a resolution regarding the thing that made them cry.
According to psychologists, crying occurs in 15-30% of all psychotherapy sessions. Because crying for a long time releases oxytocin and other feel-good chemicals that gives you a sense of calm and ease your physical and emotional pain. Around 50% of people feel better after crying, while 10% of people actually feel worse after crying. Mind-blowing crying statistics! Isn’t it?
Related: Victim Tears and Authentic Tears: How Crying Makes you Feel Better
Facts about crying – What about a “bad” cry?
Those who suppress their crying for the fear of being judged as less emotionally stable or because they felt shame, were highly likely to feel worse after they cried than they felt.
This mostly happens to people who are poor at expressing their emotions or have depressive symptoms. Such people give a bad cry and fail to trigger compassion and empathy in other people. As a result, they get no pleasure from crying.
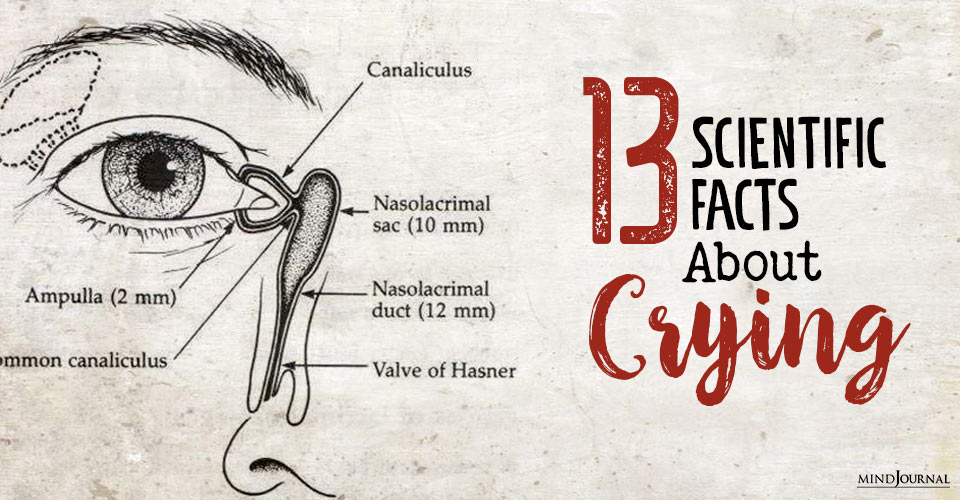
7. Why does your nose run when you cry?
Physiological facts about crying –
According to Ad Vingerhoets – a clinical psychologist, who researched human crying for more than 20 years – your nose runs even before you cry, and can certainly keep it up while you’re sobbing because your tears are simply draining.
“Most of our tears just go back into the body”, added Ad Vingerhoets, PhD.
Tears secreted from the lacrimal glands—the onion tears and the emotional ones—drain near the nose. “When the capacity of the drainage system is insufficient, then tears start flowing over your cheeks, and that’s what we call crying,” Vingerhoets said.
8. Babies cry for 1 – 3 hours every day.
Infants cry to alert their parents about serious issues like – discomfort due to extreme cold or hot temperatures in the room, hunger, thirst, boredom, a wet diaper, gas, and tiredness. Parents tend to develop an instinct that helps them decode various cries of their babies and act accordingly.
Facts about crying: If babies cry for more than 3 hours a day, more than 3 days a week, for more than 3 weeks then it is a sign of colic, which means excessive crying without a known cause.
9. Crying can become involuntary.
This is one of the most interesting facts about crying! Some people can easily turn on the waterworks to manipulate others, while some are overwhelmed by it.
But, some people tend to laugh out loud or start sobbing out of the blue, and some people are indeed more prone to crying than others.
Neurological conditions like Pseudobulbar affect also known as reflex crying or involuntary emotional expression disorder increase a person’s propensity to cry.
Surprisingly, there are some neurological conditions like Alzheimer’s disease, stroke, Lou Gehrig’s disease, and multiple sclerosis that can trigger crying along with laughing uncontrollably at inappropriate times. This is also called pathological laughing and crying (PLC).
Read: Why Do You Cry Easily: Even Without Any Reason
Other facts about tears and crying:
10. Literature on the Roman Empire highlights tears are associated with romantic pleasure, which is based on the people’s belief that lovers desired their beloved more when they cried.
11. Scientists are yet to find legit proof of emotional crying in any animal other than humans.
12. People in Bali observe tearless funerals. This is the only country to hold funeral services 2 years after the death of the person.
13. People with depression have a poor urge to cry because their pessimistic minds believe that nothing can alleviate their suffering.
I hope these scientific facts about crying have resolved some of your queries.
Did you enjoy reading these amazing facts about crying? Would you like to add any more?
Let us know in the comments below.
References:
- Laan, A.J., Van Assen, M.A. and Vingerhoets, A.J., 2012. Individual differences in adult crying: The role of attachment styles. Social Behavior and Personality: an international journal, 40(3), pp.453-471.
- Becht, M.C. and Vingerhoets, A.J., 2002. Crying and mood change: A cross-cultural study. Cognition & Emotion, 16(1), pp.87-101.
- Gračanin, A., Bylsma, L.M. and Vingerhoets, A.J., 2014. Is crying a self-soothing behavior?. Frontiers in Psychology, 5, p.502.
- Bylsma, L.M., Croon, M.A., Vingerhoets, A.J. and Rottenberg, J., 2011. When and for whom does crying improve mood? A daily diary study of 1004 crying episodes. Journal of Research in Personality, 45(4), pp.385-392.
- Schocker, L., 2014. 13 Things You Probably Don’t Know About Tears. [online] HuffPost. Available at: <https://www.huffpost.com/entry/tear-facts_n_4570879> [Accessed 5 May 2022].
- Lutz, T., 2001. Crying: The natural and cultural history of tears. WW Norton & Company.
Frequently Asked Questions (Faqs)
How does crying help?
Crying helps you by removing toxins from the body, relieving stress, and elevating your mood by lowering manganese levels. Also, crying helps you get support from people around you.
Does crying help clear skin?
Since crying can lower stress it may have a positive effect (for a short term) on your skin glow. However, excess crying can give you puffy eyes and lead to capillary damages, breakouts, or inflammation around the eye region.
What does crying symbolize?
Crying uncontrollably produces a disheveled body, symbolizing a disordered or chaotic social body. It implies a breach of social boundaries or damage to a desired interpersonal relationship.










Leave a Reply